The effects of histone deacetylase inhibitors on heterochromatin: implications for anticancer therapy?
- PMID: 15940285
- PMCID: PMC1369099
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400441
The effects of histone deacetylase inhibitors on heterochromatin: implications for anticancer therapy?
Abstract
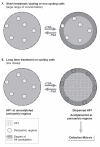
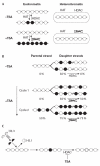
Histone acetylation regulates many chromosome functions, such as gene expression and chromosome segregation. Histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACIs) induce growth arrest, differentiation and apoptosis of cancer cells ex vivo, as well as in vivo in tumour-bearing animal models, and are now undergoing clinical trials as anti-tumour agents. However, little attention has been paid to how HDACIs function in these biological settings and why different cells respond in different ways. Here, we discuss the consequences of inhibiting histone deacetylases in cycling versus non-cycling cells, in light of the dynamics of histone acetylation patterns with a specific emphasis on heterochromatic regions of the genome.
Figures
References
-
- Almouzni G, Khochbin S, Dimitrov S, Wolffe AP (1994) Histone acetylation influences both gene expression and development of Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol 165: 654–669 - PubMed
-
- Craig JM, Earle E, Canham P, Wong LH, Anderson M, Choo KH (2003) Analysis of mammalian proteins involved in chromatin modification reveals new metaphase centromeric proteins and distinct chromosomal distribution patterns. Hum Mol Genet 12: 3109–3121 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

