Early growth response-1 transcription factor is essential for ethanol-induced fatty liver injury in mice
- PMID: 15940638
- PMCID: PMC1959407
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2005.02.065
Early growth response-1 transcription factor is essential for ethanol-induced fatty liver injury in mice
Abstract
Background & aims: Early growth response-1 (Egr-1), an immediate early gene/zinc-finger transcription factor, is required for maximal stimulation of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) transcription in response to lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Because chronic ethanol exposure sensitizes macrophages to LPS-stimulated TNF-alpha expression, we have investigated the role of Egr-1 in mediating increased LPS-stimulated TNF-alpha expression after chronic ethanol feeding. Furthermore, because TNF-alpha contributes to alcoholic liver injury, we tested the hypothesis that Egr-1 is required for the development of ethanol-induced fatty liver injury in wild type and egr-1 -/- mice.
Methods: Wild-type and egr-1 -/- mice were fed ethanol-containing diets or pair-fed control diets for 6 weeks.
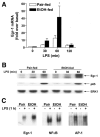
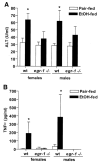
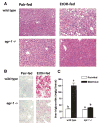
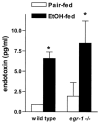
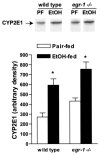
Results: Wild-type mice fed the ethanol diet developed hepatic steatosis characterized by micro- and macrovesicular lipid accumulation. However, egr-1 -/- mice did not develop steatosis after ethanol feeding. Alanine transferase and TNF-alpha concentrations in serum were increased after ethanol feeding in wild-type but not egr-1 -/- mice. In wild-type mice, challenge with LPS increased Egr-1 messenger RNA (mRNA) and DNA binding activity in liver; this response to LPS was enhanced after chronic ethanol feeding. LPS challenge also increased hepatic TNF-alpha mRNA and serum TNF-alpha to a greater extent after ethanol feeding compared with pair-fed wild-type mice. However, chronic ethanol feeding did not enhance LPS-stimulated TNF-alpha mRNA or serum TNF-alpha in egr-1 -/- mice.
Conclusions: These data show that Egr-1 contributes to increased LPS-mediated TNF-alpha expression after chronic ethanol and that the absence of Egr-1 prevents chronic ethanol-induced fatty liver, as well as increased sensitivity to LPS.
Figures


Similar articles
-
ERK1/2 and Egr-1 contribute to increased TNF-alpha production in rat Kupffer cells after chronic ethanol feeding.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2002 Jan;282(1):G6-15. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00328.2001. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2002. PMID: 11751152
-
Chronic ethanol increases lipopolysaccharide-stimulated Egr-1 expression in RAW 264.7 macrophages: contribution to enhanced tumor necrosis factor alpha production.J Biol Chem. 2002 Apr 26;277(17):14777-85. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M108967200. Epub 2002 Feb 20. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11856733
-
Early growth response-1 contributes to steatosis development after acute ethanol administration.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2012 May;36(5):759-67. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2011.01681.x. Epub 2011 Dec 5. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2012. PMID: 22141421 Free PMC article.
-
Ethanol-induced liver injury: potential roles for egr-1.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2005 Nov;29(11 Suppl):146S-150S. doi: 10.1097/01.alc.0000189286.81943.51. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2005. PMID: 16344600 Review.
-
Regulation of macrophage activation in alcoholic liver disease.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007 Jun;22 Suppl 1:S53-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2006.04650.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007. PMID: 17567466 Review.
Cited by
-
The potential of cytokines as safety biomarkers for drug-induced liver injury.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2010 Oct;66(10):961-76. doi: 10.1007/s00228-010-0862-x. Epub 2010 Aug 6. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20694460 Review.
-
Preliminary Evidence for a Relationship between Elevated Plasma TNFα and Smaller Subcortical White Matter Volume in HCV Infection Irrespective of HIV or AUD Comorbidity.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 7;22(9):4953. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094953. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34067023 Free PMC article.
-
Elk-3 Contributes to the Progression of Liver Fibrosis by Regulating the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition.Gut Liver. 2017 Jan 15;11(1):102-111. doi: 10.5009/gnl15566. Gut Liver. 2017. PMID: 27538444 Free PMC article.
-
MiRNAs in Alcohol-Related Liver Diseases and Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Step toward New Therapeutic Approaches?Cancers (Basel). 2023 Nov 23;15(23):5557. doi: 10.3390/cancers15235557. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38067261 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular and molecular mechanisms in the pathogenesis of liver fibrosis: An update.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Jun 21;20(23):7260-76. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i23.7260. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24966597 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tilg H, Diehl AM. Cytokines in alcoholic and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. N Engl J Med. 2000;343:1467–1476. - PubMed
-
- Beutler B. TNF, immunity and inflammatory disease: lessons of the past decade. J Invest Med. 1995;43:227–235. - PubMed
-
- Jacob CO. Tumor necrosis factor alpha in autoimmunity: pretty girl or old witch? Immunol Today. 1992;13:122–125. - PubMed
-
- Reimund JM, Wittersheim C, Dumont S, Muller CD, Baumann R, Poindron P, Duclos B. Mucosal inflammatory cytokine production by intestinal biopsies in patients with ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. J Clin Immunol. 1996;16:144–150. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

