Maladaptive behaviors and risk factors among the genetic subtypes of Prader-Willi syndrome
- PMID: 15940679
- PMCID: PMC1896317
- DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.a.30771
Maladaptive behaviors and risk factors among the genetic subtypes of Prader-Willi syndrome
Abstract
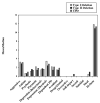
Maladaptive behaviors among 65 people with Prader-Willi syndrome were assessed using the Reiss Screen for maladaptive behaviors. Young adults in their twenties were more likely to display aggressive behavior than adolescents and older adults. Differences in maladaptive behaviors between the typical deletion and uniparental disomy (UPD) subtypes were evaluated. The typical deletion subtype had higher self-injury and stealing scores than the UPD subtype. Subject characteristics were differentially related to maladaptive behavior among the typical deletion and UPD subtypes. Differences in maladaptive behavior were also examined between the typical deletion type I and type II subtypes. The type I deletion subtype had greater physical depression scores than the type II deletion subtype. The Reiss Screen cut-off scores were used to determine whether differences occurred between the subtypes at a clinically significant level. These findings offer insight into the health care needs of people with PWS.
Copyright 2005 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Boer H, Holland AJ, Whittington JE, Butler JV, Webb T, Clarke DJ. Is psychotic illness inevitable in people with Prader-Willi syndrome due to chromosome 15 maternal uniparental disomy? Lancet. 2002;359:135–136. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

