Pseudoknots: RNA structures with diverse functions
- PMID: 15941360
- PMCID: PMC1149493
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0030213
Pseudoknots: RNA structures with diverse functions
Abstract
Just as proteins form distinct structural motifs, certain structures are commonly adopted by RNA molecules. Amongst the most prevalent is the RNA pseudoknot.
Figures
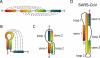
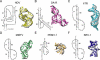
References
-
- Ke A, Zhou K, Ding F, Cate JH, Doudna JA. A conformational switch controls hepatitis delta virus ribozyme catalysis. Nature. 2004;429:201–205. - PubMed
-
- Adams PL, Stahley MR, Kosek AB, Wang J, Strobel SA. Crystal structure of a self-splicing group I intron with both exons. Nature. 2004;430:45–50. - PubMed
-
- Theimer CA, Blois CA, Feigon J. Structure of the human telomerase RNA pseudoknot reveals conserved tertiary interactions essential for function. Mol Cell. 2005;17:671–682. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

