Human T lymphotropic virus type 1 accessory protein p12I modulates calcium-mediated cellular gene expression and enhances p300 expression in T lymphocytes
- PMID: 15943569
- PMCID: PMC2668121
- DOI: 10.1089/aid.2005.21.273
Human T lymphotropic virus type 1 accessory protein p12I modulates calcium-mediated cellular gene expression and enhances p300 expression in T lymphocytes
Abstract
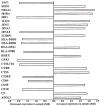
Human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1) is the etiologic agent of adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATLL), an aggressive CD4+ T lymphocyte malignancy. Activation of T lymphocytes is required for effective retroviral integration into the host cell genome and subsequent viral replication, but the molecular mechanisms involved in HTLV-1-mediated T cell activation remain unclear. HTLV-1 encodes various accessory proteins such as p12I, which has been demonstrated to be critical for HTLV-1 infectivity in vivo in rabbits and in vitro in quiescent primary human T lymphocytes. This hydrophobic protein localizes in the endoplasmic reticulum, increases intracellular calcium, and activates nuclear factor of activated T cell-mediated transcription. To further elucidate the role of p12I in regulation of cellular gene expression, we performed gene array analysis on stable p12I-expressing Jurkat T cells, using Affymetrix U133A arrays. Our data indicate that p12I altered the expression of genes associated with a network of interrelated pathways including T cell signaling, cell proliferation, and apoptosis. Expression of several calcium-regulated genes was found to be altered by p12I, consistent with known properties of the viral protein. Gene array findings were confirmed by semiquantitative RT-PCR in Jurkat T cells and primary CD4+ T lymphocytes. Furthermore, dose-dependent expression of p12I in Jurkat T cells resulted in significant increases in p300 and p300-dependent transcription. This is the first report of a viral protein influencing the transcription of p300, a rate-limiting coadapter critical in HTLV-1-mediated T cell activation. Collectively, our data strongly indicate that HTLV-1 p12I modulates cellular gene expression patterns to hasten the activation of T lymphocytes and thereby promote efficient viral infection.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Calcium-dependent enhancement of transcription of p300 by human T-lymphotropic type 1 p12I.Virology. 2006 Sep 30;353(2):247-57. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2006.06.005. Epub 2006 Jul 14. Virology. 2006. PMID: 16843515 Free PMC article.
-
Human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 p12I enhances interleukin-2 production during T-cell activation.J Virol. 2003 Oct;77(20):11027-39. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.20.11027-11039.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 14512551 Free PMC article.
-
Role of accessory proteins of HTLV-1 in viral replication, T cell activation, and cellular gene expression.Front Biosci. 2004 Sep 1;9:2556-76. doi: 10.2741/1417. Front Biosci. 2004. PMID: 15358581 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation of nuclear factor of activated T cells by human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 accessory protein p12(I).J Virol. 2002 Apr;76(7):3493-501. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.7.3493-3501.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 11884573 Free PMC article.
-
Critical role of human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 accessory proteins in viral replication and pathogenesis.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2002 Sep;66(3):396-406, table of contents. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.66.3.396-406.2002. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2002. PMID: 12208996 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Disruption of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL by viral proteins as a possible cause of cancer.Infect Agent Cancer. 2014 Dec 23;9:44. doi: 10.1186/1750-9378-9-44. eCollection 2014. Infect Agent Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25699089 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) p12I down-modulates ICAM-1 and -2 and reduces adherence of natural killer cells, thereby protecting HTLV-1-infected primary CD4+ T cells from autologous natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity despite the reduction of major histocompatibility complex class I molecules on infected cells.J Virol. 2007 Sep;81(18):9707-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00887-07. Epub 2007 Jul 3. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17609265 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Illuminating (HTLV-1)-induced adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma transcriptomic signature: A systems virology approach.Virus Res. 2023 Dec;338:199237. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2023.199237. Epub 2023 Oct 23. Virus Res. 2023. PMID: 37832654 Free PMC article.
-
Orf-I and orf-II-encoded proteins in HTLV-1 infection and persistence.Viruses. 2011 Jun;3(6):861-85. doi: 10.3390/v3060861. Epub 2011 Jun 17. Viruses. 2011. PMID: 21994758 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genotoxic consequences of viral infections.Npj Viruses. 2025 Jan 27;3(1):5. doi: 10.1038/s44298-024-00087-5. Npj Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40295867 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

