Defective insulin receptor activation and altered lipid rafts in Niemann-Pick type C disease hepatocytes
- PMID: 15943586
- PMCID: PMC1276947
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20050460
Defective insulin receptor activation and altered lipid rafts in Niemann-Pick type C disease hepatocytes
Abstract
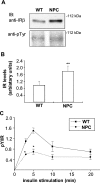
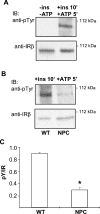
Niemann-Pick type C (NPC) disease is a neuro-visceral cholesterol storage disorder caused by mutations in the NPC-1 or NPC-2 gene. In the present paper, we studied IR (insulin receptor) activation and the plasma-membrane lipid assembly in primary hepatocytes from control and NPC1-/- mice. We have previously reported that, in hepatocytes, IR activation is dependent on cholesterol-sphingolipid rafts [Vainio, Heino, Mansson, Fredman, Kuismanen, Vaarala and Ikonen (2002) EMBO Rep. 3, 95-100]. We found that, in NPC hepatocytes, IR levels were up-regulated and the receptor activation was compromised. Defective IR activation was reproduced in isolated NPC plasma-membrane preparations, which displayed an increased cholesterol content and saturation of major phospholipids. The NPC plasma membranes were less fluid than control membranes as indicated by increased DPH (1,6-diphenyl-1,3,5-hexatriene) fluorescence anisotropy values. Both in NPC hepatocytes and plasma-membrane fractions, the association of IR with low-density DRMs (detergent-resistant membranes) was increased. Moreover, the detergent resistance of both cholesterol and phosphatidylcholine were increased in NPC membranes. Finally, cholesterol removal inhibited IR activation in control membranes but restored IR activation in NPC membranes. Taken together, the results reveal a lipid imbalance in the NPC hepatocyte, which increases lipid ordering in the plasma membrane, alters the properties of lipid rafts and interferes with the function of a raft-associated plasma-membrane receptor. Such a mechanism may participate in the pathogenesis of NPC disease and contribute to insulin resistance in other disorders of lipid metabolism.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pathological cholesterol metabolism fails to modify electrophysiological properties of afflicted neurones in Niemann-Pick disease type C.Neuroscience. 2005;130(4):867-73. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.09.065. Neuroscience. 2005. PMID: 15652985
-
Increased copper levels in in vitro and in vivo models of Niemann-Pick C disease.Biometals. 2012 Aug;25(4):777-86. doi: 10.1007/s10534-012-9546-6. Epub 2012 Apr 17. Biometals. 2012. PMID: 22526561
-
Lipid imbalance in the neurological disorder, Niemann-Pick C disease.FEBS Lett. 2006 Oct 9;580(23):5518-24. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2006.06.008. Epub 2006 Jun 15. FEBS Lett. 2006. PMID: 16797010 Review.
-
Annexin A6 is recruited into lipid rafts of Niemann-Pick type C disease fibroblasts in a Ca2+-dependent manner.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011 Feb 11;405(2):192-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.12.138. Epub 2011 Jan 7. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011. PMID: 21216236
-
Cellular pathology of Niemann-Pick type C disease.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2004 Aug;15(4):445-54. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2004.03.001. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2004. PMID: 15207834 Review.
Cited by
-
Incorporation of functional HN-F glycoprotein-containing complexes into newcastle disease virus is dependent on cholesterol and membrane lipid raft integrity.J Virol. 2007 Oct;81(19):10636-48. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01119-07. Epub 2007 Jul 25. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17652393 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of vanadium-containing compounds on membrane lipids and on microdomains used in receptor-mediated signaling.Chem Biodivers. 2008 Aug;5(8):1558-1570. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.200890144. Chem Biodivers. 2008. PMID: 18729092 Free PMC article.
-
Perturbed rhythmic activation of signaling pathways in mice deficient for Sterol Carrier Protein 2-dependent diurnal lipid transport and metabolism.Sci Rep. 2016 Apr 21;6:24631. doi: 10.1038/srep24631. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27097688 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding and Treating Niemann-Pick Type C Disease: Models Matter.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 26;21(23):8979. doi: 10.3390/ijms21238979. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33256121 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cigarette Smoke-Induced Alterations in Frontal White Matter Lipid Profiles Demonstrated by MALDI-Imaging Mass Spectrometry: Relevance to Alzheimer's Disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2016;51(1):151-63. doi: 10.3233/JAD-150916. J Alzheimers Dis. 2016. PMID: 26836183 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ikonen E., Holtta-Vuori M. Cellular pathology of Niemann-Pick type C disease. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2004;15:445–454. - PubMed
-
- Ory D. S. Niemann-Pick type C: a disorder of cellular cholesterol trafficking. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2000;1529:331–339. - PubMed
-
- Patterson M. C., Pentchev P. G. Niemann-Pick; type C. Neurology. 1996;46:1785–1786. - PubMed
-
- Reid P. C., Sugii S., Chang T. Y. Trafficking defects in endogenously synthesized cholesterol in fibroblasts, macrophages, hepatocytes, and glial cells from Niemann-Pick type C1 mice. J. Lipid Res. 2003;44:1010–1019. - PubMed
-
- Simons K., Ikonen E. Functional rafts in cell membranes. Nature (London) 1997;387:569–572. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

