APOBEC3G targets human T-cell leukemia virus type 1
- PMID: 15943885
- PMCID: PMC1156950
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-4690-2-32
APOBEC3G targets human T-cell leukemia virus type 1
Abstract
Background: Apolipoprotein B mRNA-editing enzyme-catalytic polypeptide-like 3G (APOBEC3G) is a host cellular protein with a broad antiviral activity. It inhibits infectivitiy of a wide variety of retroviruses by deaminating deoxycytidine (dC) into deoxyuridine (dU) in newly synthesized minus strand DNA, resulting in G-to-A hypermutation of the viral plus strand DNA. To clarify the mechanism of its function, we have examined the antiviral activity of APOBEC3G on human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1), the first identified human retrovirus.
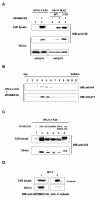
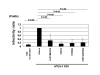
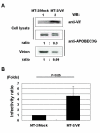
Results: In this study, we have demonstrated that overexpressed as well as endogenous APOBEC3G were incorporated into HTLV-1 virions and that APOBEC3G inhibited the infection of HTLV-1. Interestingly, several inactive mutants of APOBEC3G also inhibited HTLV-1 and no G-to-A hypermutation was induced by APOBEC3G in HTLV-1 genome. Furthermore, we introduced the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) vif gene into HTLV-1 producing cell line, MT-2, to antagonize APOBEC3G by reducing its intracellular expression and virion incorporation, which resulted in upregulation of the infectivity of produced viruses.
Conclusion: APOBEC3G is incorporated into HTLV-1 virions and inhibits the infection of HTLV-1 without exerting its cytidine deaminase activity. These results suggest that APOBEC3G might act on HTLV-1 through different mechanisms from that on HIV-1 and contribute to the unique features of HTLV-1 infection and transmission.
Figures

Comment in
-
APOBEC3G & HTLV-1: inhibition without deamination.Retrovirology. 2005 May 29;2:37. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-2-37. Retrovirology. 2005. PMID: 15921532 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
A single amino acid substitution in human APOBEC3G antiretroviral enzyme confers resistance to HIV-1 virion infectivity factor-induced depletion.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Apr 13;101(15):5652-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0400830101. Epub 2004 Mar 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15054139 Free PMC article.
-
APOBEC3G & HTLV-1: inhibition without deamination.Retrovirology. 2005 May 29;2:37. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-2-37. Retrovirology. 2005. PMID: 15921532 Free PMC article.
-
Broad antiretroviral defence by human APOBEC3G through lethal editing of nascent reverse transcripts.Nature. 2003 Jul 3;424(6944):99-103. doi: 10.1038/nature01709. Epub 2003 May 28. Nature. 2003. PMID: 12808466
-
New insights into the role of Vif in HIV-1 replication.AIDS Rev. 2004 Jan-Mar;6(1):34-9. AIDS Rev. 2004. PMID: 15168739 Review.
-
[Advances in the study of molecular mechanism of APOBEC3G anti-HIV-1].Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2008 Jul;43(7):678-82. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2008. PMID: 18819469 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
HIV-1 Vif, APOBEC, and intrinsic immunity.Retrovirology. 2008 Jun 24;5:51. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-5-51. Retrovirology. 2008. PMID: 18577210 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Frequent and recent human acquisition of simian foamy viruses through apes' bites in central Africa.PLoS Pathog. 2011 Oct;7(10):e1002306. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002306. Epub 2011 Oct 27. PLoS Pathog. 2011. PMID: 22046126 Free PMC article.
-
The MHC-II transactivator CIITA, a restriction factor against oncogenic HTLV-1 and HTLV-2 retroviruses: similarities and differences in the inhibition of Tax-1 and Tax-2 viral transactivators.Front Microbiol. 2013 Aug 22;4:234. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2013.00234. eCollection 2013. Front Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23986750 Free PMC article.
-
APOBEC3G: an intracellular centurion.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2009 Mar 12;364(1517):689-703. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2008.0193. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2009. PMID: 19008196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human cytidine deaminase APOBEC3H restricts HIV-1 replication.J Biol Chem. 2008 Apr 25;283(17):11606-14. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M707586200. Epub 2008 Feb 25. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18299330 Free PMC article.

