Drosophila ERCC1 is required for a subset of MEI-9-dependent meiotic crossovers
- PMID: 15944364
- PMCID: PMC1255914
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.104.036178
Drosophila ERCC1 is required for a subset of MEI-9-dependent meiotic crossovers
Abstract
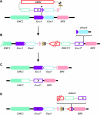
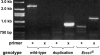
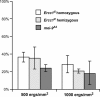
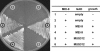
Drosophila MEI-9 is the catalytic subunit of a DNA structure-specific endonuclease required for nucleotide excision repair (NER). The enzymatic activity of this endonuclease during NER requires the presence of a second, noncatalytic subunit called ERCC1. In addition to its role in NER, MEI-9 is required for the generation of most meiotic crossovers. To better understand the role of MEI-9 in crossover formation, we report here the characterization of the Drosophila Ercc1 gene. We created an Ercc1 mutant through homologous gene targeting. We find that Ercc1 mutants are identical to mei-9 mutants in sensitivity to DNA-damaging agents, but have a less severe reduction in the number of meiotic crossovers. MEI-9 protein levels are reduced in Ercc1 mutants; however, overexpression of MEI-9 is not sufficient to restore meiotic crossing over in Ercc1 mutants. We conclude that MEI-9 can generate some meiotic crossovers in an ERCC1-independent manner.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Drosophila MUS312 interacts with the nucleotide excision repair endonuclease MEI-9 to generate meiotic crossovers.Mol Cell. 2002 Dec;10(6):1503-9. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(02)00782-7. Mol Cell. 2002. PMID: 12504024 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila hold'em is required for a subset of meiotic crossovers and interacts with the dna repair endonuclease complex subunits MEI-9 and ERCC1.Genetics. 2009 Jan;181(1):335-40. doi: 10.1534/genetics.108.093104. Epub 2008 Oct 28. Genetics. 2009. PMID: 18957705 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of Drosophila Mei-41/ATR Alters Meiotic Crossover Patterning.Genetics. 2018 Feb;208(2):579-588. doi: 10.1534/genetics.117.300634. Epub 2017 Dec 15. Genetics. 2018. PMID: 29247012 Free PMC article.
-
Meiotic MCM Proteins Promote and Inhibit Crossovers During Meiotic Recombination.Genetics. 2019 Jun;212(2):461-468. doi: 10.1534/genetics.119.302221. Epub 2019 Apr 26. Genetics. 2019. PMID: 31028111 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleotide excision repair endonuclease genes in Drosophila melanogaster.Mutat Res. 2000 Apr 28;459(3):219-28. doi: 10.1016/s0921-8777(99)00075-0. Mutat Res. 2000. PMID: 10812334
Cited by
-
A Halloween gene noppera-bo encodes a glutathione S-transferase essential for ecdysteroid biosynthesis via regulating the behaviour of cholesterol in Drosophila.Sci Rep. 2014 Oct 10;4:6586. doi: 10.1038/srep06586. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 25300303 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic lethality of Drosophila in the absence of the MUS81 endonuclease and the DmBlm helicase is associated with elevated apoptosis.Genetics. 2007 Aug;176(4):1993-2001. doi: 10.1534/genetics.106.070060. Epub 2007 Jul 1. Genetics. 2007. PMID: 17603121 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple-pathway analysis of double-strand break repair mutations in Drosophila.PLoS Genet. 2007 Apr 13;3(4):e50. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0030050. Epub 2007 Feb 21. PLoS Genet. 2007. PMID: 17432935 Free PMC article.
-
BLM helicase ortholog Sgs1 is a central regulator of meiotic recombination intermediate metabolism.Mol Cell. 2012 Apr 13;46(1):43-53. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.02.020. Mol Cell. 2012. PMID: 22500736 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila MUS312 and the vertebrate ortholog BTBD12 interact with DNA structure-specific endonucleases in DNA repair and recombination.Mol Cell. 2009 Jul 10;35(1):128-35. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.06.019. Mol Cell. 2009. PMID: 19595722 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bardwell, A. J., L. Bardwell, A. E. Tomkinson and E. C. Friedberg, 1994. Specific cleavage of model recombination and repair intermediates by the yeast Rad1-Rad10 DNA endonuclease. Science 265: 2082–2085. - PubMed
-
- Davies, A. A., E. C. Friedberg, A. E. Tomkinson, R. D. Wood and S. C. West, 1995. Role of the Rad1 and Rad10 proteins in nucleotide excision repair and recombination. J. Biol. Chem. 270: 24638–24641. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

