Serotonin 5-HT1A receptors regulate NMDA receptor channels through a microtubule-dependent mechanism
- PMID: 15944377
- PMCID: PMC6724987
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1187-05.2005
Serotonin 5-HT1A receptors regulate NMDA receptor channels through a microtubule-dependent mechanism
Abstract
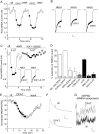
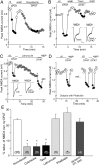
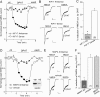
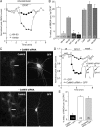
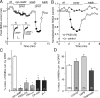
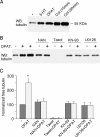
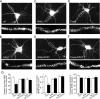
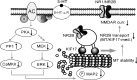
The serotonin system and NMDA receptors (NMDARs) in prefrontal cortex (PFC) are both critically involved in the regulation of cognition and emotion under normal and pathological conditions; however, the interactions between them are essentially unknown. Here we show that serotonin, by activating 5-HT(1A) receptors, inhibited NMDA receptor-mediated ionic and synaptic currents in PFC pyramidal neurons, and the NR2B subunit-containing NMDA receptor is the primary target of 5-HT(1A) receptors. This effect of 5-HT(1A) receptors was blocked by agents that interfere with microtubule assembly, as well as by cellular knock-down of the kinesin motor protein KIF17 (kinesin superfamily member 17), which transports NR2B-containing vesicles along microtubule in neuronal dendrites. Inhibition of either CaMKII (calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase II) or MEK/ERK (mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase) abolished the 5-HT(1A) modulation of NMDAR currents. Biochemical evidence also indicates that 5-HT(1A) activation reduced microtubule stability, which was abolished by CaMKII or MEK inhibitors. Moreover, immunocytochemical studies show that 5-HT(1A) activation decreased the number of surface NR2B subunits on dendrites, which was prevented by the microtubule stabilizer. Together, these results suggest that serotonin suppresses NMDAR function through a mechanism dependent on microtubule/kinesin-based dendritic transport of NMDA receptors that is regulated by CaMKII and ERK signaling pathways. The 5-HT(1A)-NMDAR interaction provides a potential mechanism underlying the role of serotonin in controlling emotional and cognitive processes subserved by PFC.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Activation of 5-HT2A/C receptors counteracts 5-HT1A regulation of n-methyl-D-aspartate receptor channels in pyramidal neurons of prefrontal cortex.J Biol Chem. 2008 Jun 20;283(25):17194-204. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M801713200. Epub 2008 Apr 28. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18442977 Free PMC article.
-
Microtubule regulation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor channels in neurons.J Biol Chem. 2005 Aug 19;280(33):29420-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M504499200. Epub 2005 Jun 23. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15975919
-
Clozapine functions through the prefrontal cortex serotonin 1A receptor to heighten neuronal activity via calmodulin kinase II-NMDA receptor interactions.J Neurochem. 2012 Feb;120(3):396-407. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07565.x. Epub 2011 Dec 15. J Neurochem. 2012. PMID: 22044428 Free PMC article.
-
Synapse regression in depression: the role of 5-HT receptors in modulating NMDA receptor function and synaptic plasticity.Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2010 Apr;44(4):301-8. doi: 10.3109/00048670903555146. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2010. PMID: 20307163 Review.
-
Membrane organization and function of the serotonin(1A) receptor.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2007 Dec;27(8):1097-116. doi: 10.1007/s10571-007-9189-2. Epub 2007 Aug 21. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2007. PMID: 17710529 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Adrenergic modulation of NMDA receptors in prefrontal cortex is differentially regulated by RGS proteins and spinophilin.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Nov 28;103(48):18338-43. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0604560103. Epub 2006 Nov 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 17101972 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of a Flavonoid-Rich Fraction on the Acquisition and Extinction of Fear Memory: Pharmacological and Molecular Approaches.Front Behav Neurosci. 2016 Jan 5;9:345. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2015.00345. eCollection 2015. Front Behav Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26778988 Free PMC article.
-
Ion Channel and Neurotransmitter Modulators as Electroceutical Approaches to the Control of Cancer.Curr Pharm Des. 2017;23(32):4827-4841. doi: 10.2174/1381612823666170530105837. Curr Pharm Des. 2017. PMID: 28554310 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SNARE proteins are essential in the potentiation of NMDA receptors by group II metabotropic glutamate receptors.J Physiol. 2013 Aug 15;591(16):3935-47. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2013.255075. Epub 2013 Jun 17. J Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23774277 Free PMC article.
-
Control of neuronal ion channel function by glycogen synthase kinase-3: new prospective for an old kinase.Front Mol Neurosci. 2012 Jul 16;5:80. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2012.00080. eCollection 2012. Front Mol Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22811658 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andrade R (1998) Regulation of membrane excitability in the central nervous system by serotonin receptor subtypes. Ann NY Acad Sci 861: 190-203. - PubMed
-
- Bantick RA, Deakin JF, Grasby PM (2001) The 5-HT1A receptor in schizophrenia: a promising target for novel atypical neuroleptics? J Psychopharmacol 15: 37-46. - PubMed
-
- Bernhardt R, Matus A (1984) Light and electron microscopic studies of the distribution of microtubule-associated protein 2 in rat brain: a difference between dendritic and axonal cytoskeletons. J Comp Neurol 226: 203-221. - PubMed
-
- Buhot MC (1997) Serotonin receptors in cognitive behaviors. Curr Opin Neurobiol 7: 243-254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
