Serotonin 5-HT1A receptors regulate NMDA receptor channels through a microtubule-dependent mechanism
- PMID: 15944377
- PMCID: PMC6724987
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1187-05.2005
Serotonin 5-HT1A receptors regulate NMDA receptor channels through a microtubule-dependent mechanism
Abstract
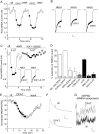
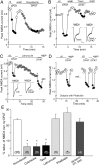
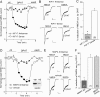
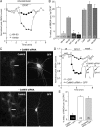
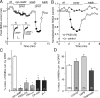
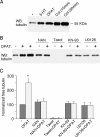
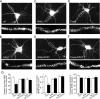
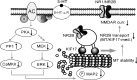
The serotonin system and NMDA receptors (NMDARs) in prefrontal cortex (PFC) are both critically involved in the regulation of cognition and emotion under normal and pathological conditions; however, the interactions between them are essentially unknown. Here we show that serotonin, by activating 5-HT(1A) receptors, inhibited NMDA receptor-mediated ionic and synaptic currents in PFC pyramidal neurons, and the NR2B subunit-containing NMDA receptor is the primary target of 5-HT(1A) receptors. This effect of 5-HT(1A) receptors was blocked by agents that interfere with microtubule assembly, as well as by cellular knock-down of the kinesin motor protein KIF17 (kinesin superfamily member 17), which transports NR2B-containing vesicles along microtubule in neuronal dendrites. Inhibition of either CaMKII (calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase II) or MEK/ERK (mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase) abolished the 5-HT(1A) modulation of NMDAR currents. Biochemical evidence also indicates that 5-HT(1A) activation reduced microtubule stability, which was abolished by CaMKII or MEK inhibitors. Moreover, immunocytochemical studies show that 5-HT(1A) activation decreased the number of surface NR2B subunits on dendrites, which was prevented by the microtubule stabilizer. Together, these results suggest that serotonin suppresses NMDAR function through a mechanism dependent on microtubule/kinesin-based dendritic transport of NMDA receptors that is regulated by CaMKII and ERK signaling pathways. The 5-HT(1A)-NMDAR interaction provides a potential mechanism underlying the role of serotonin in controlling emotional and cognitive processes subserved by PFC.
Figures


References
-
- Andrade R (1998) Regulation of membrane excitability in the central nervous system by serotonin receptor subtypes. Ann NY Acad Sci 861: 190-203. - PubMed
-
- Bantick RA, Deakin JF, Grasby PM (2001) The 5-HT1A receptor in schizophrenia: a promising target for novel atypical neuroleptics? J Psychopharmacol 15: 37-46. - PubMed
-
- Bernhardt R, Matus A (1984) Light and electron microscopic studies of the distribution of microtubule-associated protein 2 in rat brain: a difference between dendritic and axonal cytoskeletons. J Comp Neurol 226: 203-221. - PubMed
-
- Buhot MC (1997) Serotonin receptors in cognitive behaviors. Curr Opin Neurobiol 7: 243-254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
