The TetR family of transcriptional repressors
- PMID: 15944459
- PMCID: PMC1197418
- DOI: 10.1128/MMBR.69.2.326-356.2005
The TetR family of transcriptional repressors
Abstract
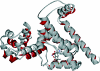
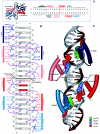
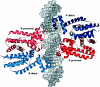
We have developed a general profile for the proteins of the TetR family of repressors. The stretch that best defines the profile of this family is made up of 47 amino acid residues that correspond to the helix-turn-helix DNA binding motif and adjacent regions in the three-dimensional structures of TetR, QacR, CprB, and EthR, four family members for which the function and three-dimensional structure are known. We have detected a set of 2,353 nonredundant proteins belonging to this family by screening genome and protein databases with the TetR profile. Proteins of the TetR family have been found in 115 genera of gram-positive, alpha-, beta-, and gamma-proteobacteria, cyanobacteria, and archaea. The set of genes they regulate is known for 85 out of the 2,353 members of the family. These proteins are involved in the transcriptional control of multidrug efflux pumps, pathways for the biosynthesis of antibiotics, response to osmotic stress and toxic chemicals, control of catabolic pathways, differentiation processes, and pathogenicity. The regulatory network in which the family member is involved can be simple, as in TetR (i.e., TetR bound to the target operator represses tetA transcription and is released in the presence of tetracycline), or more complex, involving a series of regulatory cascades in which either the expression of the TetR family member is modulated by another regulator or the TetR family member triggers a cell response to react to environmental insults. Based on what has been learned from the cocrystals of TetR and QacR with their target operators and from their three-dimensional structures in the absence and in the presence of ligands, and based on multialignment analyses of the conserved stretch of 47 amino acids in the 2,353 TetR family members, two groups of residues have been identified. One group includes highly conserved positions involved in the proper orientation of the helix-turn-helix motif and hence seems to play a structural role. The other set of less conserved residues are involved in establishing contacts with the phosphate backbone and target bases in the operator. Information related to the TetR family of regulators has been updated in a database that can be accessed at www.bactregulators.org.
Figures

References
-
- Ahlert, J., E. Shepard, N. Lomovskaya, E. Zazopoulos, A. Staffa, B. O. Bachmann, K. Huang, L. Fonstein, A. Czisny, R. E. Whitwam, C. M. Farnet, and J. S. Thorson. 2002. The calicheamicin gene cluster and its iterative type I enediyne PKS. Science 297:1173-1176. - PubMed
-
- Aigle, B., A. Wietzorrek, E. Takano, and M. J. Bibb. 2000. A single amino acid substitution in region 1.2 of the principal sigma factor of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) results in pleiotropic loss of antibiotic production. Mol. Microbiol. 37:995-1004. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

