Signalling mechanisms underlying subversion of the immune response by the filarial nematode secreted product ES-62
- PMID: 15946247
- PMCID: PMC1782160
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2005.02167.x
Signalling mechanisms underlying subversion of the immune response by the filarial nematode secreted product ES-62
Abstract
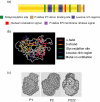
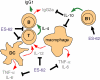
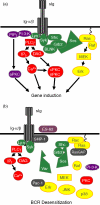
Secretion of immunomodulatory molecules is a key strategy employed by pathogens to enable their survival in host organisms. For example, arthropod-transmitted filarial nematodes, which achieve longevity within the infected host by suppressing and modulating the host immune response, produce excretory-secretory (ES) products that have been demonstrated to possess immunomodulatory properties. In this review we discuss the immunomodulatory effects of the phosphorylcholine-containing filarial nematode-secreted glycoprotein ES-62 and describe the intracellular signal transduction pathways it targets to achieve these effects.
Figures

References
-
- WHO. Filariasis. Geneva: World Health Organisation; 2000.
-
- Brattig NW. Pathogenesis and host responses in human onchocerciasis. Impact of Onchocerca filariae and Wolbachia endobacteria. Microbes Infect. 2004;6:113–28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

