Phenylephrine acts via IP3-dependent intracellular NO release to stimulate L-type Ca2+ current in cat atrial myocytes
- PMID: 15946966
- PMCID: PMC1474159
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.090035
Phenylephrine acts via IP3-dependent intracellular NO release to stimulate L-type Ca2+ current in cat atrial myocytes
Abstract
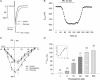
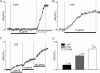
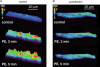
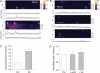
This study determined the effects of alpha1-adrenergic receptor (alpha1-AR) stimulation by phenylephrine (PE) on L-type Ca2+ current (I(Ca,L)) in cat atrial myocytes. PE (10 microm) reversibly increased I(Ca,L) (51.3%; n = 40) and shifted peak I(Ca,L) activation voltage by -10 mV. PE-induced stimulation of I(Ca,L) was blocked by each of 1 microm prazocin, 10 microm L-NIO, 10 microm W-7, 10 microm ODQ, 2 microm H-89 or 10 microm LY294002, and was unaffected by 10 microm chelerythrine or incubating cells in pertussis toxin (PTX). PE-induced stimulation of I(Ca,L) also was inhibited by each of 10 microm ryanodine or 5 microm thapsigargin, by blocking IP3 receptors with 2 microm 2-APB or 10 microm xestospongin C or by intracellular dialysis of heparin. In field-stimulated cells, PE increased intracellular NO (NOi) production. PE-induced NOi release was inhibited by each of 1 microm prazocin, 10 microm L-NIO, 10 microm W-7, 10 microm LY294002, 2 microm H-89, 10 microm ryanodine, 5 microm thapsigargin, 2 microm 2-APB or 10 microm xestospongin C, and unchanged by PTX. PE (10 microm) increased phosphorylation of Akt, which was inhibited by LY294002. Confocal microscopy showed that PE stimulated NOi release from subsarcolemmal sites and this was prevented by 2 mm methyl-beta-cyclodextrin, an agent that disrupts caveolae formation. PE also increased local, subsarcolemmal SR Ca2+ release via IP3-dependent signalling. Electron micrographs of atrial myocytes show peripheral SR cisternae in close proximity to clusters of caveolae. We conclude that in cat atrial myocytes PE acts via alpha1-ARs coupled to PTX-insensitive G-protein to release NOi, which in turn stimulates I(Ca,L). PE-induced NOi release requires stimulation of both PI-3K/Akt and IP3-dependent Ca2+ signalling. NO stimulates I(Ca,L) via cGMP-mediated cAMP-dependent PKA signalling. IP3-dependent Ca2+ signalling may enhance local SR Ca2+ release required to activate Ca2+-dependent eNOS/NOi production from subsarcolemmal caveolae sites.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Signaling mechanisms that mediate nitric oxide production induced by acetylcholine exposure and withdrawal in cat atrial myocytes.Circ Res. 2003 Dec 12;93(12):1233-40. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000106133.92737.27. Epub 2003 Nov 13. Circ Res. 2003. PMID: 14615286
-
Beta 2-adrenergic receptor signaling acts via NO release to mediate ACh-induced activation of ATP-sensitive K+ current in cat atrial myocytes.J Gen Physiol. 2002 Jan;119(1):69-82. doi: 10.1085/jgp.119.1.69. J Gen Physiol. 2002. PMID: 11773239 Free PMC article.
-
Nitric oxide signalling by selective beta(2)-adrenoceptor stimulation prevents ACh-induced inhibition of beta(2)-stimulated Ca(2+) current in cat atrial myocytes.J Physiol. 2002 Aug 1;542(Pt 3):711-23. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.023341. J Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12154173 Free PMC article.
-
L-type calcium channel targeting and local signalling in cardiac myocytes.Cardiovasc Res. 2013 May 1;98(2):177-86. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvt021. Epub 2013 Feb 14. Cardiovasc Res. 2013. PMID: 23417040 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chromogranins and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-dependent Ca(2+)-signaling in cardiomyopathy and heart failure.Curr Med Chem. 2012;19(24):4068-73. doi: 10.2174/092986712802430045. Curr Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22834797 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms of stretch-induced electro-anatomical remodeling and atrial arrhythmogenesis.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2024 Aug;193:11-24. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2024.05.011. Epub 2024 May 24. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38797242 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Caveolae, ion channels and cardiac arrhythmias.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2008 Oct-Nov;98(2-3):149-60. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2009.01.012. Epub 2009 Jan 30. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 19351512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The flavonoid luteolin induces nitric oxide production and arterial relaxation.Eur J Nutr. 2014 Feb;53(1):269-75. doi: 10.1007/s00394-013-0525-7. Epub 2013 Apr 21. Eur J Nutr. 2014. PMID: 23604495 Free PMC article.
-
Timing mechanisms to control heart rhythm and initiate arrhythmias: roles for intracellular organelles, signalling pathways and subsarcolemmal Ca2.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2023 Jun 19;378(1879):20220170. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2022.0170. Epub 2023 May 1. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37122228 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signalling mechanisms in contraction-mediated stimulation of intracellular NO production in cat ventricular myocytes.J Physiol. 2007 Apr 1;580(Pt 1):327-45. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.126805. Epub 2007 Jan 18. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17234690 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bogoyevitch MA, Fuller SJ, Sugden PH. cAMP and protein synthesis in isolated adult rat heart preparations. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 1993;265:C1247–C1257. - PubMed
-
- Bootman MD, Collins TJ, Mackenzie L, Roderick EL, Berridge MJ, Peppiatt CM. 2-Aminoethoxydiphenyl borate (2-APB) is a reliable blocker of store-operated Ca2+ entry but an inconsistent inhibitor of InsP3-induced Ca2+ release. FASEB J. 2002;16:1145–1150. - PubMed
-
- Brazil DP, Hemmings BA. Ten years of protein kinase B signalling: a hard Akt to follow. Trends Biochem Sci. 2001;26:657–664. - PubMed
-
- Brodde OE, Motomura S, Endoh M, Schumann HJ. Lack of correlation between the positive inotropic effect evoked by á-adrenoceptor stimulation and the levels of cyclic AMP and/or cyclic GMP in the isolated ventricle strip of the rabbit. J Mol Cellular Cardiol. 1978;10:207–219. - PubMed
-
- Brunner F, Schmidt K, Nielsen EB, Mayer B. Novel guanylyl cyclase inhibitor potently inhibits cyclic GMP accumulation in endothelial cells and relaxation of bovine pulmonary artery. J Pharmacol Exp Therapeutics. 1996;277:48–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

