P2X2 and P2X3 receptor expression in postnatal and adult rat urinary bladder and lumbosacral spinal cord
- PMID: 15947072
- PMCID: PMC1305916
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00234.2005
P2X2 and P2X3 receptor expression in postnatal and adult rat urinary bladder and lumbosacral spinal cord
Abstract
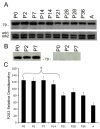
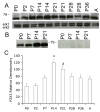
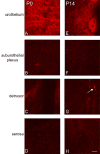
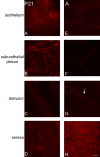
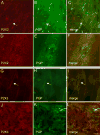
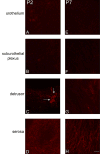
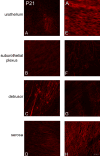
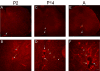
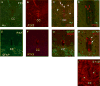
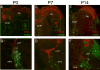
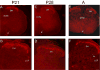
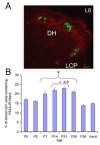
P2X receptors mediate the effects of ATP in micturition and nociception. During postnatal maturation, a spinobulbospinal reflex and voluntary voiding replace primitive voiding reflexes. This may involve changes in neuroactive compounds and receptors in bladder reflex pathways. We examined P2X2 and P2X3 receptors in bladder and spinal cord from postnatal (P0-P36, indicating number of days) and adult Wistar rats. Western blot of whole bladders for P2X2 and P2X3 expression was performed. Immunostaining for P2X2 and P2X3 receptors in urothelium and detrusor smooth muscle whole mounts and spinal cord sections was examined. Western blot demonstrated an age-dependent decrease (R(2) = 0.96, P </= 0.005) in P2X2 receptor expression in bladder, whereas P2X3 receptor expression in bladder peaked (P </= 0.005) during P14-P21. P2X2-immunoreactivity (IR) was present in urothelial cells, suburothelial plexus, detrusor smooth muscle, and serosa at birth, with staining in urothelial cells and serosa being most predominant. With increasing postnatal age, the intensity of P2X2-IR decreased in urothelial cells but increased in suburothelial plexus. P2X3-IR increased in urothelial cells and suburothelial plexus with postnatal age, whereas staining in detrusor and serosa remained relatively constant. At birth, P2X3-IR was present in the dorsal horn, lateral collateral pathway, and dorsal commissure. With increasing age, P2X3-IR was restricted to superficial dorsal horn and lateral collateral pathway. P2X2-IR was present in ependyme cells (S-100-IR) of the central canal as early as P2. These studies demonstrate plastic expression of P2X2 and P2X3 receptors in bladder and spinal cord during early postnatal development at times coincident with appearance of mature voiding patterns.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immunohistochemical study of the P2X2 and P2X3 receptor subunits in rat and monkey sensory neurons and their central terminals.Neuropharmacology. 1997 Sep;36(9):1229-42. doi: 10.1016/s0028-3908(97)00126-3. Neuropharmacology. 1997. PMID: 9364478
-
Modulation of bladder afferent signals in normal and spinal cord-injured rats by purinergic P2X3 and P2X2/3 receptors.BJU Int. 2012 Oct;110(8 Pt B):E409-14. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2012.11189.x. Epub 2012 Apr 30. BJU Int. 2012. PMID: 22540742 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous purinergic control of bladder activity via presynaptic P2X3 and P2X2/3 receptors in the spinal cord.J Neurosci. 2010 Mar 24;30(12):4503-7. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6132-09.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20335487 Free PMC article.
-
Purinoceptors as therapeutic targets for lower urinary tract dysfunction.Br J Pharmacol. 2006 Feb;147 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S132-43. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706637. Br J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16465177 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Purinergic signalling in the urinary bladder.Auton Neurosci. 2015 Sep;191:78-81. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2015.04.012. Epub 2015 Apr 30. Auton Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25979768 Review.
Cited by
-
Research Findings on Overactive Bladder.Curr Urol. 2015 May;8(1):1-21. doi: 10.1159/000365682. Epub 2015 May 20. Curr Urol. 2015. PMID: 26195957 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulatory effects of intravesical P2X2/3 purinergic receptor inhibition on lower urinary tract electromyographic properties and voiding function of female rats with moderate or severe spinal cord injury.BJU Int. 2019 Mar;123(3):538-547. doi: 10.1111/bju.14561. Epub 2018 Oct 26. BJU Int. 2019. PMID: 30255543 Free PMC article.
-
Altered expression of P2X3 in vagal and spinal afferents following esophagitis in rats.Histochem Cell Biol. 2009 Dec;132(6):585-97. doi: 10.1007/s00418-009-0639-4. Epub 2009 Sep 26. Histochem Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19784665 Free PMC article.
-
Purinergic receptor mediated calcium signalling in urothelial cells.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 6;9(1):16101. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-52531-9. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31695098 Free PMC article.
-
A possible role of the cholinergic and purinergic receptor interaction in the regulation of the rat urinary bladder function.J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2012 Mar;32(6):421-31. doi: 10.1007/s10974-012-9285-x. Epub 2012 Feb 28. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2012. PMID: 22370867
References
-
- Andersson KE, Wein AJ. Pharmacology of the lower urinary tract: basis for current and future treatments of urinary incontinence. Pharmacol Rev. 2004;56:581–631. - PubMed
-
- Barclay J, Patel S, Dorn G, Wotherspoon G, Moffatt S, Eunson L, Abdel’al S, Natt F, Hall J, Winter J, Bevan S, Wishart W, Fox A, Ganju P. Functional downregulation of P2X3 receptor subunit in rat sensory neurons reveals a significant role in chronic neuropathic and inflammatory pain. J Neurosci. 2002;22:8139–8147. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Birder LA, de Groat WC. Induction of c-fos gene expression in spinal neurons of the rat by nociceptive and non-nociceptive stimulation of the lower urinary tract. Am J Physiol. 1993;265:R643–R648. - PubMed
-
- Birder LA, Ruan HZ, Chopra B, Xiang Z, Barrick S, Buffington CA, Roppolo JR, Ford AP, de Groat WC, Burnstock G. Alterations in P2X and P2Y purinergic receptor expression in urinary bladder from normal cats and cats with interstitial cystitis. Am J Physiol. 2004;287:F1084–1091. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

