KLF2 is essential for primitive erythropoiesis and regulates the human and murine embryonic beta-like globin genes in vivo
- PMID: 15947087
- PMCID: PMC1895257
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2005-02-0674
KLF2 is essential for primitive erythropoiesis and regulates the human and murine embryonic beta-like globin genes in vivo
Abstract
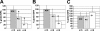
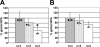
The Krüppel-like factors (KLFs) are a family of C2/H2 zinc finger DNA-binding proteins that are important in controlling developmental programs. Erythroid Krüppel-like factor (EKLF or KLF1) positively regulates the beta-globin gene in definitive erythroid cells. KLF2 (LKLF) is closely related to EKLF and is expressed in erythroid cells. KLF2-/- mice die between embryonic day 12.5 (E12.5) and E14.5, because of severe intraembryonic hemorrhaging. They also display growth retardation and anemia. We investigated the expression of the beta-like globin genes in KLF2 knockout mice. Our results show that KLF2-/- mice have a significant reduction of murine embryonic Ey- and beta h1-globin but not zeta-globin gene expression in the E10.5 yolk sac, compared with wild-type mice. The expression of the adult beta(maj)- and beta(min)-globin genes is unaffected in the fetal livers of E12.5 embryos. In mice carrying the entire human globin locus, KLF2 also regulates the expression of the human embryonic epsilon-globin gene but not the adult beta-globin gene, suggesting that this developmental-stage-specific role is evolutionarily conserved. KLF2 also plays a role in the maturation and/or stability of erythroid cells in the yolk sac. KLF2-/- embryos have a significantly increased number of primitive erythroid cells undergoing apoptotic cell death.
Figures




References
-
- Shivdasani RA, Orkin SH. The transcriptional control of hematopoiesis. Blood. 1996;87: 4025-4039. - PubMed
-
- Tsai FY, Keller G, Kuo FC, et al. An early haematopoietic defect in mice lacking the transcription factor GATA-2. Nature. 1994;371: 221-226. - PubMed
-
- Pandolfi PP, Roth ME, Karis A, et al. Targeted disruption of the GATA3 gene causes severe abnormalities in the nervous system and in fetal liver haematopoiesis. Nat Genet. 1995;11: 40-44. - PubMed
-
- Bieker JJ. Kruppel-like factors: three fingers in many pies. J Biol Chem. 2001;276: 34355-34358. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

