Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 deficiency amplifies acute lung injury in bleomycin-exposed mice
- PMID: 15947421
- PMCID: PMC2715316
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2005-0111OC
Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 deficiency amplifies acute lung injury in bleomycin-exposed mice
Abstract
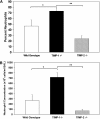
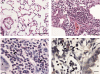
Bleomycin-induced lung injury triggers a profound and durable increase in tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase (TIMP)-1 expression, suggesting a potential role for this antiproteinase in the regulation of lung inflammation and fibrosis. TIMP-1 protein induction is spatially restricted to areas of lung injury as determined by immunohistochemistry. Using TIMP-1 null mutation mice, we demonstrate that TIMP-1 deficiency amplifies acute lung injury as determined by exaggerated pulmonary neutrophilia, hemorrhage, and vascular permeability compared with wild-type littermates after bleomycin exposure. The augmented pulmonary neutrophilia observed in TIMP-1-deficient animals was not found in similarly treated TIMP-2-deficient mice. Using TIMP-1 bone marrow (BM) chimeric mice, we observed that the TIMP-1-deficient phenotype was abolished in wild-type recipients of TIMP-1-deficient BM but not in TIMP-1-deficient recipients of wild-type BM. Acute lung injury in TIMP-1-deficient mice was accompanied by exaggerated gelatinase-B activity in the alveolar compartment. TIMP-1 deficiency did not alter neutrophil chemotactic factor accumulation in the injured lung nor neutrophil migration in response to chemotactic stimuli in vivo or in vitro. Moreover, TIMP-1 deficiency did not modify collagen accumulation after bleomycin injury. Our results provide direct evidence that TIMP-1 contributes significantly to the regulation of acute lung injury, functioning to limit inflammation and lung permeability.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Selective induction of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2001 May;24(5):599-607. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.24.5.4192. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2001. PMID: 11350830
-
TIMP-1 is a key factor of fibrogenic response to bleomycin in mouse lung.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2006 Jul-Sep;19(3):471-87. doi: 10.1177/039463200601900303. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 17026855
-
Inhibition of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells might be mediated by decreasing MMP9, TIMP-1, INF-γ and TGF-β.Cell Biochem Funct. 2015 Aug;33(6):356-66. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3118. Epub 2015 Jul 15. Cell Biochem Funct. 2015. PMID: 26178702
-
Development of pulmonary fibrosis in fibrinogen-deficient mice.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001;936:542-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2001.tb03542.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001. PMID: 11460513 Review.
-
Regulation of neutrophil activation in acute lung injury.Chest. 1999 Jul;116(1 Suppl):46S-54S. Chest. 1999. PMID: 10424590 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Pathobiology of neutrophil-epithelial interactions.Immunol Rev. 2016 Sep;273(1):94-111. doi: 10.1111/imr.12446. Immunol Rev. 2016. PMID: 27558330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Associations of circulating matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases with clinically relevant outcomes in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Data from the IPF-PRO Registry.PLoS One. 2024 Oct 17;19(10):e0312044. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0312044. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39418259 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Lung Fibrosis Resolution.Am J Pathol. 2016 May;186(5):1066-77. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2016.01.018. Epub 2016 Mar 25. Am J Pathol. 2016. PMID: 27021937 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fibrosis and cancer: do myofibroblasts come also from epithelial cells via EMT?J Cell Biochem. 2007 Jul 1;101(4):830-9. doi: 10.1002/jcb.21186. J Cell Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17211838 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating LIGHT (TNFSF14) and Interleukin-18 Levels in Sepsis-Induced Multi-Organ Injuries.Biomedicines. 2022 Jan 25;10(2):264. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10020264. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35203474 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parks WC, Wilson CL, Lopez-Boado YS. Matrix metalloproteinases as modulators of inflammation and innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 2004;4:617–629. - PubMed
-
- Ricou B, Nicod L, Lacraz S, Welgus HG, Suter PM, Dayer J-M. Matrix metalloproteinases and TIMP in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1996;154:346–352. - PubMed
-
- Hayashi T, Stetler-Stevenson WG, Fleming MV, Fishback N, Koss MN, Liotta LA, Ferrans VJ, Travis WD. Immunohistochemical study of metalloproteinases and their tissue inhibitors in the lungs of patients with diffuse alveolar damage and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Pathol 1996;149:1241–1256. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li Q, Park PW, Wilson CL, Parks WC. Matrilysin shedding of syndecan-1 regulates chemokine mobilization and transepithelial efflux of neutrophils in acute lung injury. Cell 2002;111:635–646. - PubMed
-
- Warner RL, Beltran L, Younkin EM, Lewis CS, Weiss SJ, Varani J, Johnson KJ. Role of stromelysin 1 and gelatinase B in experimental acute lung injury. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2001;24:537–544. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

