Modulation of glioma BK channels via erbB2
- PMID: 15948146
- PMCID: PMC2548405
- DOI: 10.1002/jnr.20543
Modulation of glioma BK channels via erbB2
Abstract
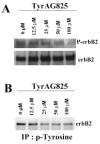
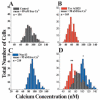
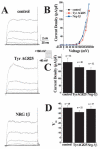
Glioma cells show up-regulation and constitutive activation of erbB2, and its expression correlates positively with increased malignancy. A similar correlation has been demonstrated for the expression of gBK, a calcium-sensitive, large-conductance K(+) channel. We show here that glioma BK channels are a downstream target of erbB2/neuregulin signaling. Tyrphostin AG825 was able to disrupt the constituitive erbB2 activation in a dose-dependent manner, causing a 30-mV positive shift in gBK channel activation in cell-attached patches. Conversely, maximal stimulation of erbB2 with a recombinant neuregulin (NRG-1beta) caused a 12-mV shift in the opposite direction. RT-PCR studies reveal no change in the BK splice variants expressed in treated glioma cells. Furthermore, isolation of surface proteins through biotinylation did not show a change in gBK channel expression, and probing with phospho-specific antibodies showed no alteration in channel phosphorylation. However, fura-II Ca(2+) fluorescence imaging revealed a 35% decrease in the free intracellular Ca(2+) concentration after erbB2 inhibition and an increase in NRG-1beta-treated cells, suggesting that the observed changes most likely were due to alterations in [Ca(2+)](i). Consistent with this conclusion, neither tyrphostin AG825 nor NRG-1beta was able to modulate gBK channels under inside-out or whole-cell recording conditions when intracellular Ca(2+) was fixed. Thus, gBK channels are a downstream target for the abundantly expressed neuregulin-1 receptor erbB2 in glioma cells. However, unlike the case in other systems, this modulation appears to occur via changes in [Ca(2+)](i) without changes in channel expression or phosphorylation. The enhanced sensitivity of gBK channels in glioma cells to small, physiological Ca(2+) changes appears to be a prerequisite for this modulation.
Figures





References
-
- Anton ES, Marchionni MA, Lee KF, Rakic P. Role of GGF/neuregulin signaling in interactions between migrating neurons and radial glia in the developing cerebral cortex. Development. 1997;124:3501–3510. - PubMed
-
- Basrai D, Kraft R, Bollensdorff C, Liebmann L, Benndorf K, Patt S. BK channel blockers inhibit potassium-induced proliferation of human astrocytoma cells. Neuroreport. 2002;13:403–407. - PubMed
-
- Bordey A, Ullrich N, Sontheimer H. Electrophysiological characterization of astrocytes and astrocytoma cells in slices from human biopsies and experimental intracranial tumors. Soc Neurosci Abstr. 1996;22:594.13.
-
- Bordey A, Sontheimer H, Trouslard J. Muscarinic activation of BK channels induces membrane oscillations in glioma cells and leads to inhibition of cell migration. J Membrane Biol. 2000;176:31–40. - PubMed
-
- Bringmann A, Biedermann B, Reichenbach A. Expression of potassium channels during postnatal differentiation of rabbit Muller glial cells. Eur J Neurosci. 1999;11:2883–2896. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

