Green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate blocks PDGF-induced proliferation and migration of rat pancreatic stellate cells
- PMID: 15948241
- PMCID: PMC4315990
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i22.3368
Green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate blocks PDGF-induced proliferation and migration of rat pancreatic stellate cells
Abstract
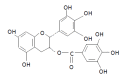
Aim: To clarify the effects of epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) on the platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-BB-induced proliferation and migration of pancreatic stellate cells (PSCs).
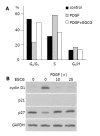
Methods: PSCs were isolated from rat pancreas tissue and used in their culture-activated, myofibroblast-like phenotype. Cell proliferation was assessed by measuring the incorporation of 5-bromo-2'-deoxyuridine. Cell migration was assessed using modified Boyden chambers. Cyclin D1, p21Waf1, and p27Kip1 expression and phosphorylation of PDGF beta-receptor, extracellular signal-regulated kinase, and Akt were examined by Western blotting. Activation of phospha-tidylinositol 3-kinase was examined by kinase assay using phosphatidylinositol as a substrate. Cell cycle was assessed by flow cytometry after staining with propidium iodide.
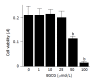
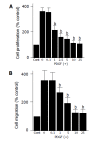
Results: EGCG at non-cytotoxic concentrations inhibited PDGF-induced proliferation and migration. This effect was associated with the inhibition of cell cycle progression beyond the G1 phase, decreased cyclin D1 and increased p27Kip1 expression. EGCG inhibited tyrosine phosphorylation of PDGF beta-receptor and downstream activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathways.
Conclusion: EGCG inhibited PDGF-BB-induced proliferation and migration of PSCs through the inhibition of PDGF-mediated signaling pathways.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits platelet-derived growth factor-induced proliferation of human hepatic stellate cell line LI90.J Hepatol. 2004 Jan;40(1):52-9. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(03)00477-x. J Hepatol. 2004. PMID: 14672614
-
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate, a green-tea polyphenol, suppresses Rho signaling in TWNT-4 human hepatic stellate cells.J Lab Clin Med. 2005 Jun;145(6):316-22. doi: 10.1016/j.lab.2005.03.017. J Lab Clin Med. 2005. PMID: 15976760
-
Suppression of extracellular signals and cell proliferation by the black tea polyphenol, theaflavin-3,3'-digallate.Carcinogenesis. 1999 Apr;20(4):733-6. doi: 10.1093/carcin/20.4.733. Carcinogenesis. 1999. PMID: 10223207
-
Green tea polyphenols: biology and therapeutic implications in cancer.Front Biosci. 2007 Sep 1;12:4881-99. doi: 10.2741/2435. Front Biosci. 2007. PMID: 17569617 Review.
-
Green tea and tea polyphenols in cancer prevention.Front Biosci. 2004 Sep 1;9:2618-31. doi: 10.2741/1421. Front Biosci. 2004. PMID: 15358585 Review.
Cited by
-
Pancreatic Stellate Cells and the Targeted Therapeutic Strategies in Chronic Pancreatitis.Molecules. 2023 Jul 22;28(14):5586. doi: 10.3390/molecules28145586. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37513458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting pancreatic stellate cells in chronic pancreatitis: Focus on therapeutic drugs and natural compounds.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Oct 19;13:1042651. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1042651. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36339568 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The research progress of anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrosis treatment of chronic pancreatitis.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 24;12:1050274. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1050274. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36505827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel therapeutic strategies targeting tumor-stromal interactions in pancreatic cancer.Front Physiol. 2013 Nov 11;4:331. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2013.00331. eCollection 2013. Front Physiol. 2013. PMID: 24273517 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) inhibits the migratory behavior of tumor bronchial epithelial cells.Respir Res. 2008 Apr 21;9(1):33. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-9-33. Respir Res. 2008. PMID: 18426555 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bachem MG, Schneider E, Gross H, Weidenbach H, Schmid RM, Menke A, Siech M, Beger H, Grünert A, Adler G. Identification, culture, and characterization of pancreatic stellate cells in rats and humans. Gastroenterology. 1998;115:421–432. - PubMed
-
- Masamune A, Kikuta K, Satoh M, Sakai Y, Satoh A, Shimosegawa T. Ligands of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma block activation of pancreatic stellate cells. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:141–147. - PubMed
-
- Masamune A, Sakai Y, Kikuta K, Satoh M, Satoh A, Shimosegawa T. Activated rat pancreatic stellate cells express intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) in vitro. Pancreas. 2002;25:78–85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

