Modelling approaches to dose estimation in children
- PMID: 15948929
- PMCID: PMC1884869
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2005.02429.x
Modelling approaches to dose estimation in children
Abstract
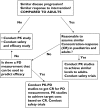
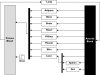
Most of the drugs on the market are originally developed for adults and dosage selection is based on an optimal balance between clinical efficacy and safety. The aphorism 'children are not small adults' not only holds true for the selection of suitable drugs and dosages for use in children but also their susceptibility to adverse drug reactions. Since children may not be subject to dose escalation studies similar to those carried out in the adult population, some initial estimation of dose in paediatrics should be obtained via extrapolation approaches. However, following such an exercise, well-conducted PK-PD or PK studies will still be needed to determine the most appropriate doses for neonates, infants, children and adolescents.
Figures


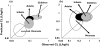
References
-
- Johnson TN. The development of drug metabolising enzymes and their influence on the susceptibility to adverse drug reactions in children. Toxicology. 2003;192:37–48. - PubMed
-
- Breant V, Charpiat B, Sab JM, Maire P, Jelliffe RW. How many patients and blood levels are necessary for population pharmacokinetic analysis? Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1996;51:283–8. - PubMed
-
- Lee PID. Design and power of a population pharmacokinetic study. Pharm Res. 2001;18:75–82. - PubMed
-
- Johnson TN, Rostami-Hodjegan A, Goddard JM, Tanner MS, Tucker GT. Contribution of midazolam and its 1-hydroxy metabolite to pre-operative sedation in children: a pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic analysis. Br J Anaesth. 2002;89:428–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

