Satellog: a database for the identification and prioritization of satellite repeats in disease association studies
- PMID: 15949044
- PMCID: PMC1181805
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-6-145
Satellog: a database for the identification and prioritization of satellite repeats in disease association studies
Abstract
Background: To date, 35 human diseases, some of which also exhibit anticipation, have been associated with unstable repeats. Anticipation has been reported in a number of diseases in which repeat expansion may have a role in etiology. Despite the growing importance of unstable repeats in disease, currently no resource exists for the prioritization of repeats. Here we present Satellog, a database that catalogs all pure 1-16 repeat unit satellite repeats in the human genome along with supplementary data. Satellog analyzes each pure repeat in UniGene clusters for evidence of repeat polymorphism.
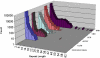
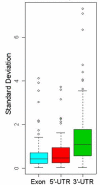
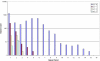
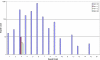
Results: A total of 5,546 such repeats were identified, providing the first indication of many novel polymorphic sites in the genome. Overall, polymorphic repeats were over-represented within 3'-UTR sequence relative to 5'-UTR and coding sequence. Interestingly, we observed that repeat polymorphism within coding sequence is restricted to trinucleotide repeats whereas UTR sequence tolerated a wider range of repeat period polymorphisms. For each pure repeat we also calculate its repeat length percentile rank, its location either within or adjacent to EnsEMBL genes, and its expression profile in normal tissues according to the GeneNote database.
Conclusion: Satellog provides the ability to dynamically prioritize repeats based on any of their characteristics (i.e. repeat unit, class, period, length, repeat length percentile rank, genomic co-ordinates), polymorphism profile within UniGene, proximity to or presence within gene regions (i.e. cds, UTR, 15 kb upstream etc.), metadata of the genes they are detected within and gene expression profiles within normal human tissues. Unstable repeats associated with 31 diseases were analyzed in Satellog to evaluate their common repeat properties. The utility of Satellog was highlighted by prioritizing repeats for Huntington's disease and schizophrenia. Satellog is available online at http://satellog.bcgsc.ca.
Figures
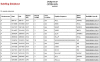
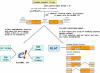
References
-
- Verkerk AJ, Pieretti M, Sutcliffe JS, Fu YH, Kuhl DP, Pizzuti A, Reiner O, Richards S, Victoria MF, Zhang FP, et al. Identification of a gene (FMR-1) containing a CGG repeat coincident with a breakpoint cluster region exhibiting length variation in fragile X syndrome. Cell. 1991;65:905–914. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90397-H. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kremer EJ, Pritchard M, Lynch M, Yu S, Holman K, Baker E, Warren ST, Schlessinger D, Sutherland GR, Richards RI. Mapping of DNA instability at the fragile X to a trinucleotide repeat sequence p(CCG)n. Science. 1991;252:1711–1714. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

