Stem cells in the dog heart are self-renewing, clonogenic, and multipotent and regenerate infarcted myocardium, improving cardiac function
- PMID: 15951423
- PMCID: PMC1157041
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0502678102
Stem cells in the dog heart are self-renewing, clonogenic, and multipotent and regenerate infarcted myocardium, improving cardiac function
Abstract
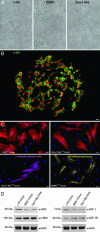
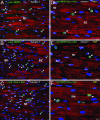
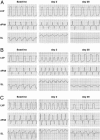
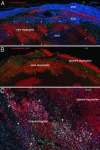
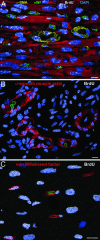
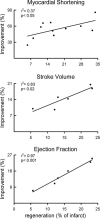
The purpose of this study was to determine whether the heart in large mammals contains cardiac progenitor cells that regulate organ homeostasis and regenerate dead myocardium after infarction. We report that the dog heart possesses a cardiac stem cell pool characterized by undifferentiated cells that are self-renewing, clonogenic, and multipotent. These clonogenic cells and early committed progeny possess a hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)-c-Met and an insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1)-IGF-1 receptor system that can be activated to induce their migration, proliferation, and survival. Therefore, myocardial infarction was induced in chronically instrumented dogs implanted with sonomicrometric crystals in the region of the left ventricular wall supplied by the occluded left anterior descending coronary artery. After infarction, HGF and IGF-1 were injected intramyocardially to stimulate resident cardiac progenitor cells. This intervention led to the formation of myocytes and coronary vessels within the infarct. Newly generated myocytes expressed nuclear and cytoplasmic proteins specific of cardiomyocytes: MEF2C was detected in the nucleus, whereas alpha-sarcomeric actin, cardiac myosin heavy chain, troponin I, and alpha-actinin were identified in the cytoplasm. Connexin 43 and N-cadherin were also present. Myocardial reconstitution resulted in a marked recovery of contractile performance of the infarcted heart. In conclusion, the activation of resident primitive cells in the damaged dog heart can promote a significant restoration of dead tissue, which is paralleled by a progressive improvement in cardiac function. These results suggest that strategies capable of activating the growth reserve of the myocardium may be important in cardiac repair after ischemic injury.
Figures
References
-
- Rosenthal, N. (2003) N. Engl. J. Med. 349, 267–274. - PubMed
-
- Anversa, P., Sussman, M. A. & Bolli, R. (2004) Circulation 109, 2832–2838. - PubMed
-
- Balsam, L. B., Wagers, A. J., Christensen, J. L., Kofidis, T., Weissman, I. L. & Robbins, R. (2004) Nature 428, 668–673. - PubMed
-
- Murry, C. E., Soonpaa, M. H., Reinecke, H., Nakajima, H., Nakajima, H. O., Rubart, M., Pasumarthi, K. B., Virag, J. I., Bartelmez, S. H., Poppa, V., et al. (2004) Nature 428, 664–668. - PubMed
-
- Kajstura, J., Rota, M., Whang, B., Cascapera, S., Hosoda, T., Bearzi, C., Nurzynska, D., Kasahara, H., Zias H., Bonafe, M., et al. (2005) Circ. Res. 96, 127–137. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AG017042/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL050142/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AG-15756/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HL-43023/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL038132/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AG-023071/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HL-66923/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL043023/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AG-17042/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HL-081737/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-38132/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-50142/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL065577/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG023071/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HL-65577/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL065573/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL081737/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL-65573/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

