PIKE GTPase signaling and function
- PMID: 15951849
- PMCID: PMC1142212
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.1.44
PIKE GTPase signaling and function
Abstract
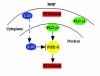
PIKE (PI 3-Kinase Enhancer) is a recently identified brain specific nuclear GTPase, which binds PI 3-kinase and stimulates its lipid kinase activity. Nerve growth factor treatment leads to PIKE activation by triggering the nuclear translocation of phospholipase C-gamma1 (PLC-gamma1), which acts as a physiologic guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) for PIKE through its SH3 domain. To date, three forms of PIKE have been characterized: PIKE-S, PIKE-L and PIKE-A. PIKE-S is initially identified shorter isoform. PIKE-L, a longer isoform of PIKE gene, differs from PIKE-S by C-terminal extension containing Arf-GAP (ADP ribosylation factor-GTPase Activating Protein) and two ankyrin repeats domains. In contrast to the exclusive nuclear localization of PIKE-S, PIKE-L occurs in both the nucleus and the cytoplasm. PIKE-L physiologically associates with Homer 1, an mGluR I binding adaptor protein. The Homer/PIKE-L complex couples PI 3-kinase to mGluR I and regulates a major action of group I mGluRs, prevention of neuronal apoptosis. More recently, a third PIKE isoform, PIKE-A was identified in human glioblastoma multiforme brain cancers. Unlike the brain specific PIKE-L and -S isoforms, PIKE-A distributes in various tissues. PIKE-A contains the same domains present in PIKE-L but lacks N-terminal proline-rich domain (PRD), which binds PI 3-kinase and PLC-gamma1. Instead, PIKE-A specifically binds to active Akt and upregulates its activity in a GTP-dependent manner, mediating human cancer cell invasion and preventing apoptosis. Thus, PIKE extends its roles from the nucleus to the cytoplasm, mediating cellular processes from cell invasion to programmed cell death.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Ye K. et al. Pike. A nuclear gtpase that enhances PI3kinase activity and is regulated by protein 4.1N. Cell. 2000;103:919–30. - PubMed
-
- Ye K. et al. Phospholipase Cγ1 is a physiological guanine nucleotide exchange factor for the nuclear GTPase PIKE. Nature. 2002;415:541–544. - PubMed
-
- Cukierman E. et al. The ARF1 GTPase-activating protein: zinc finger motif and Golgi complex localization. Science. 1995;270:1999–2002. - PubMed
-
- Rong R. et al. PI3 kinase enhancer-Homer complex couples mGluRI to PI3 kinase, preventing neuronal apoptosis. Nat Neurosci. 2003;6:1153–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

