Precise temporal modulation in the response of the SOS DNA repair network in individual bacteria
- PMID: 15954802
- PMCID: PMC1151601
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0030238
Precise temporal modulation in the response of the SOS DNA repair network in individual bacteria
Abstract
The SOS genetic network is responsible for the repair/bypass of DNA damage in bacterial cells. While the initial stages of the response have been well characterized, less is known about the dynamics of the response after induction and its shutoff. To address this, we followed the response of the SOS network in living individual Escherichia coli cells. The promoter activity (PA) of SOS genes was monitored using fluorescent protein-promoter fusions, with high temporal resolution, after ultraviolet irradiation activation. We find a temporal pattern of discrete activity peaks masked in studies of cell populations. The number of peaks increases, while their amplitude reaches saturation, as the damage level is increased. Peak timing is highly precise from cell to cell and is independent of the stage in the cell cycle at the time of damage. Evidence is presented for the involvement of the umuDC operon in maintaining the pattern of PA and its temporal precision, providing further evidence for the role UmuD cleavage plays in effecting a timed pause during the SOS response, as previously proposed. The modulations in PA we observe share many features in common with the oscillatory behavior recently observed in a mammalian DNA damage response. Our results, which reveal a hitherto unknown modulation of the SOS response, underscore the importance of carrying out dynamic measurements at the level of individual living cells in order to unravel how a natural genetic network operates at the systems level.
Figures

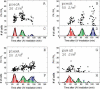

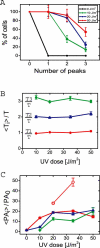
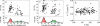
Comment in
-
After 30 years of study, the bacterial SOS response still surprises us.PLoS Biol. 2005 Jul;3(7):e255. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0030255. Epub 2005 Jul 12. PLoS Biol. 2005. PMID: 16000023 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Little JW. The SOS regulatory system. In: Lin ECC, Simon A, editors. Regulation of gene expression in Escherichia coli. Austin (Texas): Landes; 1996. pp. 453–479.
-
- Friedberg EC, Walker GC, Siede W. DNA repair and mutagenesis. Washington (DC): ASM Press; 1995. 698 pp.
-
- Fernandez de Henestrosa AR, Ogi T, Aoyagi S, Chafin D, Hayes JJ. Identification of additional genes belonging to the LexA regulon in Escherichia coli . Mol Microbiol. 2000;35:1560–1572. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

