Down-regulation of 7SL RNA expression and impairment of vesicular protein transport pathways by Leishmania infection of macrophages
- PMID: 15955815
- PMCID: PMC3089017
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M504162200
Down-regulation of 7SL RNA expression and impairment of vesicular protein transport pathways by Leishmania infection of macrophages
Abstract
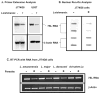
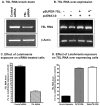
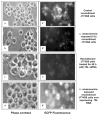
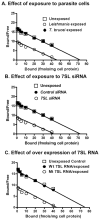
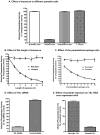
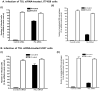
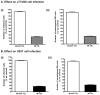
The parasitic protozoan Leishmania specifically manipulates the expression of host macrophage genes during initial interactions, as revealed by mRNA differential display reverse transcription-PCR and cDNA microarray analyses. The genes that are down-regulated in mouse (J774G8) or human (U937) macrophages upon exposure to Leishmania include small RNA transcripts from the short interspersed element sequences. Among the short interspersed element RNAs that are down-regulated is 7SL RNA, which is the RNA component of the signal recognition particle. Because the microbicidal functions of macrophages profoundly count on vesicular protein transport processes, down-regulation of 7SL RNA may be significant in the establishment of infection by Leishmania in macrophage phagolysosomes. To evaluate whether down-regulation of 7SL RNA results in inhibition of signal recognition particle-mediated vesicular protein transport processes, we have tested and found that the targeting of proteins to the endoplasmic reticulum and plasma membrane and the secretion of proteins by macrophages are compromised in Leishmania-infected J774G8 and U937 cells. Knocking down 7SL RNA using small interfering RNA mimicked the effect of exposure of macrophages to Leishmania. The overexpression of 7SL RNA in J774G8 or U937 cells made these cells resistant to Leishmania infection, suggesting the possible biological significance of down-regulation of 7SL RNA synthesis in the establishment of infection by Leishmania. We conclude that Leishmania down-regulates 7SL RNA in macrophages to manipulate the targeting of many proteins that use the vesicular transport pathway and thus favors its successful establishment of infection in macrophages.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Leishmania-induced repression of selected non-coding RNA genes containing B-box element at their promoters in alternatively polarized M2 macrophages.Mol Cell Biochem. 2011 Apr;350(1-2):47-57. doi: 10.1007/s11010-010-0681-5. Epub 2010 Dec 17. Mol Cell Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21165676
-
Differential expression of B1-containing transcripts in Leishmania-exposed macrophages.J Biol Chem. 2000 Jun 23;275(25):19428-32. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M001336200. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10781585 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of down-regulation of RNA polymerase III-transcribed non-coding RNA genes in macrophages by Leishmania.J Biol Chem. 2011 Feb 25;286(8):6614-26. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.181735. Epub 2010 Dec 13. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21149457 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of macrophage subsets and cytokine production in leishmaniasis.Cytokine. 2021 Nov;147:155309. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2020.155309. Epub 2020 Dec 14. Cytokine. 2021. PMID: 33334669 Review.
-
The role of Bax in the apoptosis of Leishmania-infected macrophages.Microb Pathog. 2020 Feb;139:103892. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2019.103892. Epub 2019 Nov 25. Microb Pathog. 2020. PMID: 31778755 Review.
Cited by
-
The paradigm of intracellular parasite survival and drug resistance in leishmanial parasite through genome plasticity and epigenetics: Perception and future perspective.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Feb 6;13:1001973. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1001973. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36814446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional Intricacy and Symmetry of Long Non-Coding RNAs in Parasitic Infections.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Oct 8;11:751523. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.751523. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34692567 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Leishmania-induced repression of selected non-coding RNA genes containing B-box element at their promoters in alternatively polarized M2 macrophages.Mol Cell Biochem. 2011 Apr;350(1-2):47-57. doi: 10.1007/s11010-010-0681-5. Epub 2010 Dec 17. Mol Cell Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21165676
-
Model-based Evaluation of Gene Expression Changes in Response to Leishmania Infection.Gene Regul Syst Bio. 2019 Feb 6;13:1177625019828350. doi: 10.1177/1177625019828350. eCollection 2019. Gene Regul Syst Bio. 2019. PMID: 30792575 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploiting Long Noncoding RNAs as Pharmacological Targets to Modulate Epigenetic Diseases.Yale J Biol Med. 2017 Mar 29;90(1):73-86. eCollection 2017 Mar. Yale J Biol Med. 2017. PMID: 28356895 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kane MM, Mosser DM. Curr Opin Hematol. 2000;7:26–31. - PubMed
-
- Handman E, Bullen DV. Trends Parasitol. 2002;18:332–334. - PubMed
-
- Denkers EY, Butcher BA. Trends Parasitol. 2005;21:35–41. - PubMed
-
- Solbach W, Laskay T. Adv Immunol. 2000;74:275–317. - PubMed
-
- Bogdan C, Gessner A, Solbach W, Röllinghoff M. Curr Opin Immunol. 1996;8:517–525. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

