G protein beta interacts with the glucocorticoid receptor and suppresses its transcriptional activity in the nucleus
- PMID: 15955845
- PMCID: PMC2171637
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200409150
G protein beta interacts with the glucocorticoid receptor and suppresses its transcriptional activity in the nucleus
Abstract
Extracellular stimuli that activate cell surface receptors modulate glucocorticoid actions via as yet unclear mechanisms. Here, we report that the guanine nucleotide-binding protein (G protein)-coupled receptor-activated WD-repeat Gbeta interacts with the glucocorticoid receptor (GR), comigrates with it into the nucleus and suppresses GR-induced transactivation of the glucocorticoid-responsive genes. Association of Ggamma with Gbeta is necessary for this action of Gbeta. Both endogenous and enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP)-fused Gbeta2 and Ggamma2 proteins were detected in the nucleus at baseline, whereas a fraction of EGFP-Gbeta2 and DsRed2-GR comigrated to the nucleus or the plasma membrane, depending on the exposure of cells to dexamethasone or somatostatin, respectively. Gbeta2 was associated with GR/glucocorticoid response elements (GREs) in vivo and suppressed activation function-2-directed transcriptional activity of the GR. We conclude that the Gbetagamma complex interacts with the GR and suppresses its transcriptional activity by associating with the transcriptional complex formed on GR-responsive promoters.
Figures

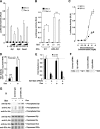
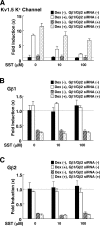
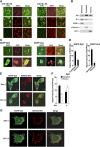
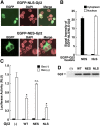
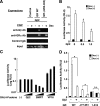
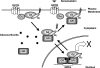
References
-
- Brown, P.J., and A. Schonbrunn. 1993. Affinity purification of a somatostatin receptor-G-protein complex demonstrates specificity in receptor-G-protein coupling. J. Biol. Chem. 268:6668–6676. - PubMed
-
- Cabrera-Vera, T.M., J. Vanhauwe, T.O. Thomas, M. Medkova, A. Preininger, M.R. Mazzoni, and H.E. Hamm. 2003. Insights into G protein structure, function, and regulation. Endocr. Rev. 24:765–781. - PubMed
-
- Chang, B.Y., M. Chiang, and C.A. Cartwright. 2001. The interaction of Src and RACK1 is enhanced by activation of protein kinase C and tyrosine phosphorylation of RACK1. J. Biol. Chem. 276:20346–20356. - PubMed
-
- Chen, S., E.J. Dell, F. Lin, J. Sai, and H.E. Hamm. 2004. RACK1 regulates specific functions of Gbetagamma. J. Biol. Chem. 279:17861–17868. - PubMed
-
- Chrousos, G.P. 1995. The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and immune-mediated inflammation. N. Engl. J. Med. 332:1351–1362. - PubMed

