A positive feedback loop between Dumbfounded and Rolling pebbles leads to myotube enlargement in Drosophila
- PMID: 15955848
- PMCID: PMC2171639
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200501126
A positive feedback loop between Dumbfounded and Rolling pebbles leads to myotube enlargement in Drosophila
Abstract
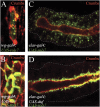
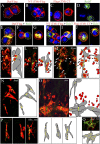
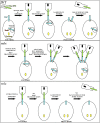
In Drosophila, myoblasts are subdivided into founders and fusion-competent myoblasts (fcm) with myotubes forming through fusion of one founder and several fcm. Duf and rolling pebbles 7 (Rols7; also known as antisocial) are expressed in founders, whereas sticks and stones (SNS) is present in fcm. Duf attracts fcm toward founders and also causes translocation of Rols7 from the cytoplasm to the fusion site. We show that Duf is a type 1 transmembrane protein that induces Rols7 translocation specifically when present intact and engaged in homophilic or Duf-SNS adhesion. Although its membrane-anchored extracellular domain functions as an attractant and is sufficient for the initial round of fusion, subsequent fusions require replenishment of Duf through cotranslocation with Rols7 tetratricopeptide repeat/coiled-coil domain-containing vesicles to the founder/myotube surface, causing both Duf and Rols7 to be at fusion sites between founders/myotubes and fcm. This implicates the Duf-Rols7 positive feedback loop to the occurrence of fusion at specific sites along the membrane and provides a mechanism by which the rate of fusion is controlled.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Drosophila rolling pebbles colocalises and putatively interacts with alpha-Actinin and the Sls isoform Zormin in the Z-discs of the sarcomere and with Dumbfounded/Kirre, alpha-Actinin and Zormin in the terminal Z-discs.J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2006;27(1):93-106. doi: 10.1007/s10974-006-9060-y. Epub 2006 Apr 20. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2006. PMID: 16699917
-
Drosophila rolling pebbles: a multidomain protein required for myoblast fusion that recruits D-Titin in response to the myoblast attractant Dumbfounded.Dev Cell. 2001 Nov;1(5):691-703. doi: 10.1016/s1534-5807(01)00075-2. Dev Cell. 2001. PMID: 11709189
-
The intracellular domain of Dumbfounded affects myoblast fusion efficiency and interacts with Rolling pebbles and Loner.PLoS One. 2010 Feb 23;5(2):e9374. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009374. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20186342 Free PMC article.
-
Myoblast fusion in Drosophila.Bioessays. 2002 Jul;24(7):591-601. doi: 10.1002/bies.10115. Bioessays. 2002. PMID: 12111720 Review.
-
Cell and molecular biology of myoblast fusion.Int Rev Cytol. 2003;225:33-89. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(05)25002-7. Int Rev Cytol. 2003. PMID: 12696590 Review.
Cited by
-
The complex spatio-temporal regulation of the Drosophila myoblast attractant gene duf/kirre.PLoS One. 2009 Sep 9;4(9):e6960. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006960. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19742310 Free PMC article.
-
Invasive podosomes and myoblast fusion.Curr Top Membr. 2011;68:235-58. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-385891-7.00010-6. Curr Top Membr. 2011. PMID: 21771502 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
The actin nucleator WASp is required for myoblast fusion during adult Drosophila myogenesis.Development. 2011 Jun;138(11):2347-57. doi: 10.1242/dev.055012. Development. 2011. PMID: 21558381 Free PMC article.
-
The MARVEL domain protein, Singles Bar, is required for progression past the pre-fusion complex stage of myoblast fusion.Dev Biol. 2007 Jul 15;307(2):328-39. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.04.045. Epub 2007 May 3. Dev Biol. 2007. PMID: 17537424 Free PMC article.
-
Visualizing new dimensions in Drosophila myoblast fusion.Bioessays. 2008 May;30(5):423-31. doi: 10.1002/bies.20756. Bioessays. 2008. PMID: 18404690 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abmayr, S.M., L. Balagopalan, B.J. Galletta, and S.J. Hong. 2003. Cell and molecular biology of myoblast fusion. Int. Rev. Cytol. 225:33–89. - PubMed
-
- Artero, R.D., I. Castanon, and M.K. Baylies. 2001. The immunoglobulin-like protein Hibris functions as a dose-dependent regulator of myoblast fusion and is differentially controlled by Ras and Notch signaling. Development. 128:4251–4264. - PubMed
-
- Bate, M. 1990. The embryonic development of larval muscles in Drosophila. Development. 110:791–804. - PubMed
-
- Baylies, M.K., M. Bate, and G.M. Ruiz. 1998. Myogenesis: a view from Drosophila. Cell. 93:921–927. - PubMed
-
- Bour, B.A., M.A. O'Brien, W.L. Lockwood, E.S. Goldstein, R. Bodmer, P.H. Taghert, S.M. Abmayr, and H.T. Nguyen. 1995. Drosophila MEF2, a transcription factor that is essential for myogenesis. Genes Dev. 9:730–741. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

