Transfer and evaluation of an automated, low-cost real-time reverse transcription-PCR test for diagnosis and monitoring of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection in a West African resource-limited setting
- PMID: 15956387
- PMCID: PMC1151915
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.43.6.2709-2717.2005
Transfer and evaluation of an automated, low-cost real-time reverse transcription-PCR test for diagnosis and monitoring of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection in a West African resource-limited setting
Abstract
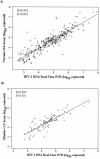
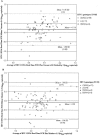
There is an urgent need for low-cost human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) viral load (VL) monitoring technologies in resource-limited settings. An automated TaqMan real-time reverse transcription-PCR (RT-PCR) assay was transferred to the laboratory of the Centre de Diagnostic et de Recherches sur le SIDA, Abidjan, Côte d'Ivoire, and assessed for HIV-1 RNA VL testing in 806 plasma samples collected within four ANRS research programs. The detection threshold and reproducibility of the assay were first determined. The quantitative results obtained with this assay were compared with two commercial HIV-1 RNA kits (the Versant version 3.0 and Monitor version 1.5 assays) in specimens harboring mainly the circulating recombinant form 02 strain (CRF02). The clinical evaluation of this test was done in different situations including the early diagnosis of pediatric infection and the monitoring of antiretroviral-treated patients. The quantification limit of our method was 300 copies/ml. The HIV-1 RNA values obtained by real-time PCR assay were highly correlated with those obtained by the Versant kit (r = 0.901; P < 0.001) and the Monitor test (r = 0.856; P < 0.001) and homogeneously distributed according to HIV-1 genotypes. For the early diagnosis of pediatric HIV-1 infection, the sensitivity and specificity of the real-time PCR assay were both 100% (95% confidence intervals of 93.7 to 100.0 and 98.3 to 100.0, respectively), compared to the Versant results. Following initiation of antiretroviral treatment, the kinetics of HIV-1 RNA levels were very comparable, with a similar proportion of adults and children below the detection limit during follow-up with our technique and the Versant assay. The TaqMan real-time PCR (12 dollars per test) is now routinely used to monitor HIV-1 infection in our laboratory. This technology should be further evaluated in limited-resource countries where strains other than CRF02 are prevalent.
Figures


References
-
- Bland, J. M., and D. J. Altman. 1995. Comparing methods of measurement: why plotting difference against standard method is misleading. Lancet 346:1085-1087. - PubMed
-
- Bonard, D., F. Rouet, T. A. Toni, A. Minga, C. Huet, D. K. Ekouevi, F. Dabis, R. Salamon, and C. Rouzioux. 2003. Field evaluation of an improved assay using a heat-dissociated p24 antigen for adults mainly infected with HIV-1CRF02_AG strains in Cote d'Ivoire, West Africa. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. Hum. Retrovirol. 34:267-273. - PubMed
-
- Braun, J., J. C. Plantier, M. F. Hellot, E. Tuaillon, M. Gueudin, F. Damond, A. Malmsten, G. E. Corrigan, and F. Simon. 2003. A new quantitative HIV load assay based on plasma virion reverse transcriptase activity for the different types, groups and subtypes. AIDS 17:331-336. - PubMed
-
- Crowe, S., S. Turnbull, R. Oelrichs, and A. Dunne. 2003. Monitoring of human immunodeficiency virus infection in resource-constrained countries. Clin. Infect. Dis. 37:S25-S35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

