MR diffusion tensor imaging and fiber tracking in spinal cord compression
- PMID: 15956535
- PMCID: PMC8149058
MR diffusion tensor imaging and fiber tracking in spinal cord compression
Abstract
Background and purpose: Spinal cord damage can result in major functional disability. Alteration of the spinal cord structural integrity can be assessed by using diffusion tensor imaging methods. Our objective is to evaluate the diagnostic accuracy of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), fractional anisotropy (FA), and fiber tracking in both acute and slowly progressive spinal cord compressions.
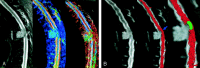
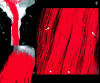
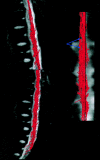
Methods: Fifteen patients with clinical symptoms of acute (n = 2) or slowly progressive (n = 13) spinal cord compression and 11 healthy volunteers were prospectively selected. We performed T2-weighted fast spin echo (FSE) and diffusion tensor imaging by using a 1.5-T MR scanner. ADC and FA maps were computed. Regions of interest were placed at the cervical, upper and lower thoracic cord levels for the healthy subjects and on the area with abnormal T2-weighted signal intensity in the patients with cord compression. In three patients, we used fiber tracking to locate the areas of cord compression precisely. Data were analyzed by using a mixed model. The sensitivity (SE) and specificity (sp) of imaging (T2, ADC, and FA maps) in the detection of spinal cord abnormality were statistically evaluated.
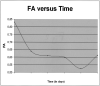
Results: For the healthy subjects, averaged ADC values ranged from 0.96 10(-3) mm(2)/s to 1.05 10(-3) mm(2)/s and averaged FA values ranged from 0.745 to 0.751. Ten patients had decreased FA (0.67 +/- 0.087), and one had increased FA values (0.831); only two patients had increased ADC values (1.03 +/- 0.177). There was a statistically significant difference in the FA values between volunteers and patients (P = .012). FA had a much higher sensitivity (SE = 73.3%) and specificity (sp = 100%) in spinal cord abnormalities detection compared with T2-weighted FSE imaging (se = 46.7%, sp = 100%) and ADC (SE = 13.4%, sp = 80%).
Conclusions: FA has the highest sensitivity and specificity in the detection of acute spinal cord abnormalities. Spinal cord fiber tracking is a useful tool to focus measurements on the compressed spinal cord.
Figures
Comment in
-
Comparison between diffusion tensor imaging and conventional MR imaging sequences in the detection of spinal cord abnormalities.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007 May;28(5):806-7. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007. PMID: 17571452 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Takahashi M, Yamashita Y, Sakamoto Y, Kojima R. Chronic cervical cord compression: clinical significance of increased signal intensity on MR images. Radiology 1989;173:219–224 - PubMed
-
- Demir A, Ries M, Moonen C, et al. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging with apparent diffusion coefficient and apparent diffusion tensor maps in cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Radiology 2003;229:37–43 - PubMed
-
- Matsumoto M, Toyama Y, Ishikawa M, et al. Increased signal intensity of the spinal cord on magnetic resonance images in cervical compressive myelopathy. Spine 2000;25:677–682 - PubMed
-
- Ries M, Jones R, Dousset V, Moonen C. Diffusion tensor MRI of the spinal cord. Magn Reson Med 2000;44:884–892 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
