Preliminary physical mapping of RNA-RNA linkages in the genomic RNA of Moloney murine leukemia virus
- PMID: 15956559
- PMCID: PMC1143758
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.13.8142-8148.2005
Preliminary physical mapping of RNA-RNA linkages in the genomic RNA of Moloney murine leukemia virus
Abstract
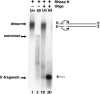
Retrovirus particles contain two copies of their genomic RNA, held together in a dimer by linkages which presumably consist of a limited number of base pairs. In an effort to localize these linkages, we digested deproteinized RNA from Moloney murine leukemia virus (MLV) particles with RNase H in the presence of oligodeoxynucleotides complementary to specific sites in viral RNA. The cleaved RNAs were then characterized by nondenaturing gel electrophoresis. We found that fragments composed of nucleotides 1 to 754 were dimeric, with a linkage as thermostable as that between dimers of intact genomic RNA. In contrast, there was no stable linkage between fragments consisting of nucleotides 755 to 8332. Thus, the most stable linkage between monomers is on the 5' side of nucleotide 754. This conclusion is in agreement with earlier electron microscopic analyses of partially denatured viral RNAs and with our study (C. S. Hibbert, J. Mirro, and A. Rein, J. Virol. 78:10927-10938, 2004) of encapsidated nonviral mRNAs containing inserts of viral sequence. We obtained similar results with RNAs from immature MLV particles, in which the dimeric linkage is different from that in mature particles and has not previously been localized. The 5' and 3' fragments of cleaved RNA are all held together by thermolabile linkages, indicating the presence of tethering interactions between bases 5' and bases 3' of the cleavage site. When RNAs from mature particles were cleaved at nucleotide 1201, we detected tethering interactions spanning the cleavage site which are intramonomeric and are as strong as the most stable linkage between the monomers.
Figures
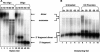
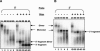

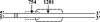

Similar articles
-
mRNA molecules containing murine leukemia virus packaging signals are encapsidated as dimers.J Virol. 2004 Oct;78(20):10927-38. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.20.10927-10938.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15452213 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a high affinity nucleocapsid protein binding element within the Moloney murine leukemia virus Psi-RNA packaging signal: implications for genome recognition.J Mol Biol. 2001 Nov 23;314(2):217-32. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2001.5139. J Mol Biol. 2001. PMID: 11718556
-
An additional dimer linkage structure in Moloney murine leukemia virus RNA.J Mol Biol. 1999 Aug 20;291(3):603-13. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1999.2984. J Mol Biol. 1999. PMID: 10448040
-
How retroviruses select their genomes.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2005 Aug;3(8):643-55. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1210. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16064056 Review.
-
The structure-function relationship of the enterovirus 3'-UTR.Virus Res. 2009 Feb;139(2):209-16. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2008.07.014. Epub 2008 Aug 30. Virus Res. 2009. PMID: 18706945 Review.
Cited by
-
HIV-1 RNA dimerization: It takes two to tango.AIDS Rev. 2009 Apr-Jun;11(2):91-102. AIDS Rev. 2009. PMID: 19529749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selective and nonselective packaging of cellular RNAs in retrovirus particles.J Virol. 2007 Jun;81(12):6623-31. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02833-06. Epub 2007 Mar 28. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17392359 Free PMC article.
-
An RNA structural switch regulates diploid genome packaging by Moloney murine leukemia virus.J Mol Biol. 2010 Feb 12;396(1):141-52. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2009.11.033. Epub 2009 Nov 17. J Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 19931283 Free PMC article.
-
Two distinct Moloney murine leukemia virus RNAs produced from a single locus dimerize at random.Virology. 2006 Jan 20;344(2):391-400. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2005.09.002. Epub 2005 Oct 10. Virology. 2006. PMID: 16216294 Free PMC article.
-
Structural polymorphism of the HIV-1 leader region explored by computational methods.Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Dec 20;33(22):7151-63. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki1015. Print 2005. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005. PMID: 16371347 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bender, W., and N. Davidson. 1976. Mapping of poly(A) sequences in the electron microscope reveals unusual structure of type C oncornavirus RNA molecules. Cell 7:595-607. - PubMed
-
- Berkowitz, R., J. Fisher, and S. P. Goff. 1996. RNA packaging. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 214:177-218. - PubMed
-
- Darlix, J. L., C. Gabus, M. T. Nugeyre, F. Clavel, and F. Barre-Sinoussi. 1990. cis elements and trans-acting factors involved in the RNA dimerization of the human immunodeficiency virus HIV-1. J. Mol. Biol. 216:689-699. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

