Role of insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor signalling in cancer
- PMID: 15956962
- PMCID: PMC2361813
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602627
Role of insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor signalling in cancer
Abstract
The insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1) signalling is highly implicated in cancer. In this signalling the IGF-1 receptor (IGF-1R) is unquestionable, the predominating single factor. IGF-1R is crucial for tumour transformation and survival of malignant cell, but is only partially involved in normal cell growth. This is in part due to the interactions with oncogenes. Recent findings suggest a close interplay with the p53/MDM2 pathway. Disturbances in components in the p53/MDM2/IGF-1R network may cause IGF-1R upregulation and growth advantage for the cancer cell. Targeting of IGF-1R is more and more seen as a promising option for future cancer therapy. Single chain antibodies and small molecules with selective effects on IGF-1R dependent malignant growth are of particular interest. Forthcoming clinical trials are welcome and will indeed be the only way to evaluate the impact of IGF-1R targeting in human cancer.
Figures
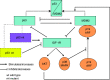
Republished in
-
Role of insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor signalling in cancer.Br J Cancer. 2007;96 Suppl:R2-6. Br J Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17393577
Similar articles
-
Role of insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor signalling in cancer.Br J Cancer. 2007;96 Suppl:R2-6. Br J Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17393577
-
Targeting the insulin-like growth factor receptor-1R pathway for cancer therapy.Clin Cancer Res. 2010 May 1;16(9):2512-7. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-2232. Epub 2010 Apr 13. Clin Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20388853
-
A novel role for IGF-1R in p53-mediated apoptosis through translational modulation of the p53-Mdm2 feedback loop.J Cell Biol. 2007 Sep 10;178(6):995-1007. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200703044. J Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17846171 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of hematologic malignancies and solid tumors by inhibiting IGF receptor signaling.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2005 Jun;5(3):487-99. doi: 10.1586/14737140.5.3.487. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2005. PMID: 16001956 Review.
-
The insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor in cancer: old focus, new future.Eur J Cancer. 2007 Sep;43(13):1895-904. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2007.05.021. Epub 2007 Jul 10. Eur J Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17624760 Review.
Cited by
-
IGF1R signalling is a guardian of self-tolerance restricting autoantibody production.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 29;13:958206. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.958206. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36105797 Free PMC article.
-
Long-Term IGF1 Stimulation Leads to Cellular Senescence via Functional Interaction with the Thioredoxin-Interacting Protein, TXNIP.Cells. 2022 Oct 17;11(20):3260. doi: 10.3390/cells11203260. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36291127 Free PMC article.
-
Sustained proliferation in cancer: Mechanisms and novel therapeutic targets.Semin Cancer Biol. 2015 Dec;35 Suppl(Suppl):S25-S54. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2015.02.006. Epub 2015 Apr 17. Semin Cancer Biol. 2015. PMID: 25892662 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alteration of ribosome function upon 5-fluorouracil treatment favors cancer cell drug-tolerance.Nat Commun. 2022 Jan 10;13(1):173. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-27847-8. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35013311 Free PMC article.
-
Gastrointestinal stromal tumors: management of metastatic disease and emerging therapies.Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2013 Oct;27(5):905-20. doi: 10.1016/j.hoc.2013.07.007. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2013. PMID: 24093167 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- All-Ericsson C, Girnita L, Seregard S, Bartolazzi A, Jager MJ, Larsson O (2002) Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor in uveal melanoma: a predictor for metastatic disease and a potential therapeutic target. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 43: 1–8 - PubMed
-
- Andrews DW, Resnicoff M, Flanders AE, Kenyon L, Curtis M, Merli G, Baserga R, Iliakis G, Aiken RD (2001) Results of a pilot study involving the use of an antisense oligodeoxynucleotide directed against the insulin-like growth factor type I receptor in malignant astrocytomas. J Clin Oncol 19: 2189–2200 - PubMed
-
- Baserga R (1994) Oncogenes and the strategy of growth factors. Cell 79: 927–930 - PubMed
-
- Baserga R (1999) The IGF-I receptor in cancer research. Exp Cell Res 253: 1–6 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

