Conditional rhythmicity of ventral spinal interneurons defined by expression of the Hb9 homeodomain protein
- PMID: 15958737
- PMCID: PMC6724883
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0274-05.2005
Conditional rhythmicity of ventral spinal interneurons defined by expression of the Hb9 homeodomain protein
Abstract
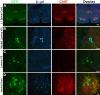
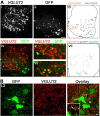
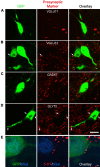
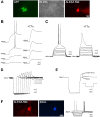
The properties of mammalian spinal interneurons that underlie rhythmic locomotor networks remain poorly described. Using postnatal transgenic mice in which expression of green fluorescent protein is driven by the promoter for the homeodomain transcription factor Hb9, as well as Hb9-lacZ knock-in mice, we describe a novel population of glutamatergic interneurons located adjacent to the ventral commissure from cervical to midlumbar spinal cord levels. Hb9+ interneurons exhibit strong postinhibitory rebound and demonstrate pronounced membrane potential oscillations in response to chemical stimuli that induce locomotor activity. These data provide a molecular and physiological delineation of a small population of ventral spinal interneurons that exhibit homogeneous electrophysiological features, the properties of which suggest that they are candidate locomotor rhythm-generating interneurons.
Figures


References
-
- Aizenman CD, Linden DJ (1999) Regulation of the rebound depolarization and spontaneous firing patterns of deep nuclear neurons in slices of rat cerebellum. J Neurophysiol 82: 1697-1709. - PubMed
-
- Arber S, Han B, Mendelsohn M, Smith M, Jessell TM, Sockanathan S (1999) Requirement for the homeobox gene Hb9 in the consolidation of motor neuron identity. Neuron 23: 659-674. - PubMed
-
- Arshavsky YI, Deliagina TG, Orlovsky GN, Panchin YV, Popova LB, Sadreyev RI (1998) Analysis of the central pattern generator for swimming in the mollusk Clione Ann NY Acad Sci 860: 51-69. - PubMed
-
- Baev KV, Degtiarenko AM, Zavadskaia TV, Kostiuk PG (1979) Impulse activity of interneurons of the lumbar portion of the spinal cord during the late long discharges in the motor nerves of immobilized thalamic cats. Neirofiziologiia 11: 236-244. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
