B cell targeted therapies
- PMID: 15960817
- PMCID: PMC2833972
- DOI: 10.1186/ar1738
B cell targeted therapies
Abstract
Although the precise pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) remains unclear, many cell populations, including monocytes, macrophages, endothelial cells, fibroblasts and B cells, participate in the inflammatory process. Ongoing research continues to evaluate the critical roles played by B cells in sustaining the chronic inflammatory process of RA. These findings have contributed to the development of targeted therapies that deplete B cells, such as rituximab, as well as inhibitors of B lymphocyte stimulation, such as belimumab. In a phase I trial, belimumab treatment significantly reduced CD20+ levels in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Phase I and phase II trials of rituximab found that rituximab plus methotrexate achieved significantly better American College of Rheumatology 50% responses for patients with RA than those patients receiving monotherapy with methotrexate. These clinical trial data present promising evidence for B cell targeted therapies as future therapeutic options for RA.
Figures
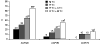

References
-
- Furie R, Stohl W, Ginzler E, Becker M, Mishra N, Chatham W, Merrill JT, Weinstein A, McCune WJ, Zhong J. Safety, pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic results of a phase 1 single and double dose-escalation study of LymphoStat-B (human monoclonal antibody to BLyS) in SLE patients [abstract 922] Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48(Suppl):S377.
-
- Edwards J. Possible new treatment for rheumatoid arthritis [abstract] Pharm J. 2000;265:676.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

