Unmet needs in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 15960819
- PMCID: PMC2833970
- DOI: 10.1186/ar1736
Unmet needs in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Until the pathophysiology/etiology of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is better understood, treatment strategies must focus on disease management. Early diagnosis and treatment with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) are necessary to reduce early joint damage, functional loss, and mortality. Several clinical trials have now clearly shown that administering appropriate DMARDs early yields better therapeutic outcomes. However, RA is a heterogeneous disease in which responses to treatment vary considerably for any given patient. Thus, choosing which patients receive combination DMARDs, and which combinations, remains one of our major challenges in treating RA patients. In many well controlled clinical trials methotrexate and other DMARDs, including the tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitors, have shown considerable efficacy in controlling the inflammatory process, but many patients continue to have active disease. Optimizing clinical response requires the use of a full spectrum of clinical agents with different therapeutic targets. Newer therapies, such as rituximab, that specifically target B cells have emerged as viable treatment options for patients with RA.
Figures
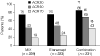
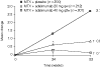
References
-
- Goekoop-Ruiterman YPM, Vries-Bouwstra K, Van Zeben D, Kerstens PJS, Hazes JMW, Zwinderman AH, Breedveld FC, Allaart CF, Dijkmans BAC. Program Book Supplement to the 2004 ACR/ARHP Annual Scientific Meeting; 16–21 October 2004; San Antonio, TX. Abstract L4. Hoboken NJ: John Wiley & Sons; 2004. Treatment strategies in early rheumatoid arthritis: clinical and radiological outcomes after 2 year follow-up of the BsSt study [abstract]
-
- Breedveld FC, Kavanaugh AF, Cohen SB, Pavelka K, van Vollen-haven R, Perez JL, Spencer-Green GT, Weisman MH. Program Book Supplement to the 2004 ACR/ARHP Annual Scientific Meeting; 16–21 October 2004; San Antonio, TX. Abstract L5. Hoboken NJ: John Wiley & Sons; 2004. Early treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with adalimumab plus methotraxate vs. adalimumab alone or methotrexate alone: the PREMIER study [abstract]
-
- van der Heijde D, Klareskog L, Wajdula J, Pedersen R, Fatenejad S, for the TEMPO Study Investigators. Program Book Supplement to the 2004 ACR/ARHP Annual Scientific Meeting; 16–21 October 2004; San Antonio, TX. Abstract L11. Hoboken NJ: John Wiley & Sons; 2004. Halting of radiographic progression in RA patients treated with etanercept and methotrexate: year 2 results from the TEMPO trial [abstract]
-
- St Clair EW, van der Heijde DMFM, Smolen JS, Maini RN, Bathon JM, Emery P, Keystone E, Schiff M, Kalden JR, Wang B. Active Controlled Study of Patient Receiving Infliximab for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis of Early Onset Study Group. Combination of infliximab and methotrexate therapy for early rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized, controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50:3432–3443. doi: 10.1002/art.20568. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

