A single air dive reduces arterial endothelial function in man
- PMID: 15961424
- PMCID: PMC1464788
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.089862
A single air dive reduces arterial endothelial function in man
Abstract
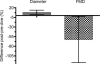
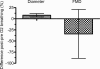
During and after decompression from dives, gas bubbles are regularly observed in the right ventricular outflow tract. A number of studies have documented that these bubbles can lead to endothelial dysfunction in the pulmonary artery but no data exist on the effect of diving on arterial endothelial function. The present study investigated if diving or oxygen breathing would influence endothelial arterial function in man. A total of 21 divers participated in this study. Nine healthy experienced male divers with a mean age of 31 +/- 5 years were compressed in a hyperbaric chamber to 280 kPa at a rate of 100 kPa min(-1) breathing air and remaining at pressure for 80 min. The ascent rate during decompression was 9 kPa min(-1) with a 7 min stop at 130 kPa (US Navy procedure). Another group of five experienced male divers (31 +/- 6 years) breathed 60% oxygen (corresponding to the oxygen tension of air at 280 kPa) for 80 min. Before and after exposure, endothelial function was assessed in both groups as flow-mediated dilatation (FMD) by ultrasound in the brachial artery. The results were compared to data obtained from a group of seven healthy individuals of the same age who had never dived. The dive produced few vascular bubbles, but a significant arterial diameter increase from 4.5 +/- 0.7 to 4.8 +/- 0.8 mm (mean +/- s.d.) and a significant reduction of FMD from 9.2 +/- 6.9 to 5.0 +/- 6.7% were observed as an indication of reduced endothelial function. In the group breathing oxygen, arterial diameter increased significantly from 4.4 +/- 0.3 mm to 4.7 +/- 0.3 mm, while FMD showed an insignificant decrease. Oxygen breathing did not decrease nitroglycerine-induced dilatation significantly. In the normal controls the arterial diameter and FMD were 4.1 +/- 0.4 mm and 7.7 +/- 0.2.8%, respectively. This study shows that diving can lead to acute arterial endothelial dysfunction in man and that oxygen breathing will increase arterial diameter after return to breathing air. Further studies are needed to determine if these mechanisms are involved in tissue injury following diving.
Figures
References
-
- Behnke AR. Decompression sickness following exposure to high pressures. In: Fulton JF, editor. Decompression Sickness. Philadelphia: Saunders; 1951. pp. 53–89.
-
- Brodsky SV, Zhang F, Nasjletti A, Goligorsky MS. Endothelium-derived microparticles impair endothelial function in vitro. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2004;286:H1910–H1915. - PubMed
-
- Brubakk AO, Eftedal O. Comparison of three different ultrasonic methods for quantification of intravascular gas bubbles. Undersea Hyperb Med. 2001;28:131–136. - PubMed
-
- Celermajer DS, Sorensen KE, Bull C, Robinson J, Deanfield JE. Endothelium-dependent dilation in the systemic arteries of asymptomatic subjects relates to coronary risk factors and their interaction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1994;24:1468–1474. - PubMed
-
- Corretti MC, Anderson TJ, Benjamin EJ, Celermajer D, Charbonneau F, Creager MA, Deanfield J, Drexler H, Gerhard-Herman M, Herrington D, Vallance P, Vita J, Vogel R. Guidelines for the ultrasound assessment of endothelial-dependent flow-mediated vasodilation of the brachial artery: a report of the International Brachial Artery Reactivity Task Force. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002;39:257–265. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

