White blood cell counts and malaria
- PMID: 15962228
- PMCID: PMC2481386
- DOI: 10.1086/431152
White blood cell counts and malaria
Abstract
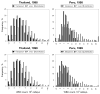
White blood cells (WBCs) were counted in 4697 individuals who presented to outpatient malaria clinics in Maesod, Tak Province, Thailand, and Iquitos, Peru, between 28 May and 28 August 1998 and between 17 May and 9 July 1999. At each site and in each year, WBC counts in the Plasmodium falciparum-infected patients were lower than those in the Plasmodium vivax-infected patients, which, in turn, were lower than those in the uninfected patients. In Thailand, one-sixth of the P. falciparum-infected patients had WBC counts of <4000 cells/microL. Leukopenia may confound population studies that estimate parasite densities on the basis of an assumed WBC count of 8000 cells/microL. For instance, in the present study, use of this conventional approach would have overestimated average asexual parasite densities in the P. falciparum-infected patients in Thailand by nearly one-third.
Figures
Comment in
-
White blood cell counts in Plasmodium vivax malaria.J Infect Dis. 2005 Nov 1;192(9):1675-6; author reply 1676-7. doi: 10.1086/496993. J Infect Dis. 2005. PMID: 16206089 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bain BJ. Blood cells. Oxford: Blackwell Science; 2002.
-
- Sokal RR, Rohlf FJ. Biometry. New York: WH Freeman; 1981.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous