Levocetirizine has a longer duration of action on improving total nasal symptoms score than fexofenadine after single administration
- PMID: 15963090
- PMCID: PMC1884902
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2005.02377.x
Levocetirizine has a longer duration of action on improving total nasal symptoms score than fexofenadine after single administration
Abstract
Aims: To compare the onset and duration of action of the new antihistamine levocetirizine with that of the second-generation antihistamine fexofenadine using the Vienna Challenge Chamber (VCC). The latter is an environment where subjects can be exposed to specific aeroallergens in controlled and reproducible conditions allowing for precise comparisons of anti-allergic drugs.
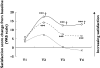
Methods: Ninety-four subjects received a single dose of levocetirizine 5 mg, fexofenadine 120 mg or placebo in a random order using a three-way cross-over design. On day 1, subjects were exposed to grass pollens (1500 grains/m(3)) in the VCC over a period of 4 h. Treatment was given 2 h after the start of challenge. On day 2, 22 h after drug intake, subjects were again exposed to pollens for 6 h. Specified symptoms were assessed by the subjects every 15 min using 5-point scales. The main efficacy parameter was the change from baseline in the Major Symptom Complex Score (MSCS = sum of rhinorrhea, sneezing, itchy nose and eyes).
Results: Baseline characteristics, including symptoms scores, were similar in the three study groups. During the first 2 h after drug intake both antihistamines achieved clinically relevant and significant (P < 0.001) improvements in symptom scores. Twenty-two to 24 h after drug intake, mean (SEM) MSCS reductions were: 1.9 (0.3) after placebo (baseline of 9.7), 3.8 (0.3) after fexofenadine (baseline of 9.9), and 5.1 (0.3) after levocetirizine (baseline of 9.8). Levocetirizine was significantly (P < 0.001) more effective than fexofenadine with a score difference of 1.3 (95% CI 0.7, 1.9). This was maintained until the end of the study (up to 28 h).
Conclusions: A rapid onset of action in alleviating seasonal allergic rhinitis (SAR) symptoms of subjects exposed to grass pollens in the VCC was observed after levocetirizine and fexofenadine. Levocetirizine was more effective than fexofenadine at and later than 22 h after drug intake, an indication of the longer-duration of action of levocetirizine.
Figures



 ), levocetirizine (▴)
), levocetirizine (▴)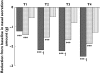
 ), placebo (
), placebo ( )
)
References
-
- Skoner DP. Allergic rhinitis. definition, epidemiology, pathophysiology, detection, and diagnosis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001;108(1 Suppl):S2–8. - PubMed
-
- Stuck BA, Czajowski J, Hagner AE, Klimek L, Verse T, Hörmann K, Maurer JT. Changes in daytime sleepiness, quality of life, and objective sleep patterns in seasonal allergic rhinitis: a controlled clinical trial. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004;113:663–8. - PubMed
-
- Crystal-Peters J, Crown WH, Goetzel RZ, Schutt DC. The cost of productivity losses associated with allergic rhinitis. Am J Manag Care. 2000;6:373–8. - PubMed
-
- Casale TB, Blaiss MS, Gelfand E, Gilmore T, Harvey PD, Hindmarch I, Simons ER, Spangler DL, Szefler SJ, Terndrup TE, Waldman SA, Weiler J, Wong DF. First do no harm: managing antihistamine impairment in patients with allergic rhinitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003;111:S835–42. - PubMed
-
- Gillard M, Christophe B, Wels B, Peck M, Massingham R, Chatelain P. H1 antagonists: receptor affinity versus selectivity. Inflamm Res. 2003;52(Suppl 1):S49–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

