A 63 element 1.75 dimensional ultrasound phased array for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia
- PMID: 15963237
- PMCID: PMC1175852
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-925X-4-39
A 63 element 1.75 dimensional ultrasound phased array for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia
Abstract
Background: Prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia are very common diseases in older American men, thus having a reliable treatment modality for both diseases is of great importance. The currently used treating options, mainly surgical ones, have numerous complications, which include the many side effects that accompany such procedures, besides the invasive nature of such techniques. Focused ultrasound is a relatively new treating modality that is showing promising results in treating prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia. Thus this technique is gaining more attention in the past decade as a non-invasive method to treat both diseases.
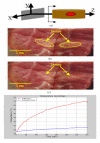
Methods: In this paper, the design, construction and evaluation of a 1.75 dimensional ultrasound phased array to be used for treating prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia is presented. With this array, the position of the focus can be controlled by changing the electrical power and phase to the individual elements for electronically focusing and steering in a three dimensional volume. The array was designed with a maximum steering angle of +/- 13.5 degrees in the transverse direction and a maximum depth of penetration of 11 cm, which allows the treatment of large prostates. The transducer piezoelectric ceramic, matching layers and cable impedance have been designed for maximum power transfer to tissue.
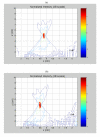
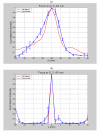
Results: To verify the capability of the transducer for focusing and steering, exposimetry was performed and the results correlated well with the calculated field. Ex vivo experiments using bovine tissue were performed with various lesion sizes and indicated the capability of the transducer to ablate tissue using short sonications.
Conclusion: A 1.75 dimensional array, that overcame the drawbacks associated with one-dimensional arrays, has been designed, built and successfully tested. Design issues, such as cable and ceramic capacitances, were taken into account when designing this array. The final prototype overcame also the problem of generating grating lobes at unwanted locations by tapering the array elements.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Two-dimensional ultrasound phased array design for tissue ablation for treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia.Int J Hyperthermia. 2004 Feb;20(1):7-31. doi: 10.1080/0265673031000150867. Int J Hyperthermia. 2004. PMID: 14612311
-
Intracavitary ultrasound phased arrays for prostate thermal therapies: MRI compatibility and in vivo testing.Med Phys. 1998 Dec;25(12):2392-9. doi: 10.1118/1.598450. Med Phys. 1998. PMID: 9874833
-
High power transcranial beam steering for ultrasonic brain therapy.Phys Med Biol. 2003 Aug 21;48(16):2577-89. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/48/16/301. Phys Med Biol. 2003. PMID: 12974575 Free PMC article.
-
[High-intensity focused ultrasound transducer].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2009 Jun;26(3):667-70. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2009. PMID: 19634694 Review. Chinese.
-
Histological changes of minimally invasive procedures for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate cancer: clinical implications.J Urol. 2003 Jul;170(1):12-9. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000072200.22089.c3. J Urol. 2003. PMID: 12796636 Review.
Cited by
-
Removing atherosclerotic plaque created using high cholesterol diet in rabbit using ultrasound.J Ther Ultrasound. 2015 Jan 29;3(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s40349-015-0025-8. eCollection 2015. J Ther Ultrasound. 2015. PMID: 25648586 Free PMC article.
-
MRI-compatible positioning device for guiding a focused ultrasound system for transrectal treatment of prostate cancer.Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2014 Jul;9(4):745-53. doi: 10.1007/s11548-013-0964-x. Epub 2013 Dec 13. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2014. PMID: 24337790
-
Optimization of ultrasound array designs for high intensity focused treatment of prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia.Med Biol Eng Comput. 2009 Jun;47(6):635-40. doi: 10.1007/s11517-009-0478-4. Epub 2009 Mar 27. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2009. PMID: 19326161
-
Coregistered three-dimensional ultrasound and photoacoustic imaging system for ovarian tissue characterization.J Biomed Opt. 2009 Sep-Oct;14(5):054014. doi: 10.1117/1.3233916. J Biomed Opt. 2009. PMID: 19895116 Free PMC article.
-
Three-axis MR-conditional robot for high-intensity focused ultrasound for treating prostate diseases transrectally.J Ther Ultrasound. 2015 Jan 29;3:2. doi: 10.1186/s40349-014-0023-2. eCollection 2015. J Ther Ultrasound. 2015. PMID: 25657846 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barrett D. Mayo Clinic on prostate health. 1. Rochester, Minn: Mayo Clinic; New York; 2000.
-
- Hutchinson E. PhD thesis. Massachusetts Institute of Technology; 1997. Intracavitary ultrasound phased arrays for thermal therapies.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

