Aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated transcription: ligand-dependent recruitment of estrogen receptor alpha to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-responsive promoters
- PMID: 15964790
- PMCID: PMC1156992
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.13.5317-5328.2005
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated transcription: ligand-dependent recruitment of estrogen receptor alpha to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-responsive promoters
Abstract
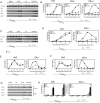
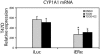
Using chromatin immunoprecipitation assays, we studied the 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD)-mediated recruitment of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) and several co-regulators to the CYP1A1 promoter. AhR displayed a time-dependent recruitment, reaching a peak at 75 min and maintaining promoter occupancy for the remainder of the time course. Recruitment of AhR was followed by TIF2/SRC2, which preceded CBP, histone H3 acetylation, and RNA polymerase II (RNAPII). Simultaneous recruitment to the enhancer and the TATA box region suggests the formation of a large multiprotein complex bridging the two promoter regions. Interestingly, estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) displayed a TCDD- and time-dependent recruitment to the CYP1A1 promoter, which was increased by co-treatment with estradiol. Transfection in HuH7 human liver cells confirmed previously reported ERalpha enhancement of AhR activity. In contrast, TCDD did not induce the recruitment of ERalpha to the estrogen-responsive pS2 promoter, and after 120 min of co-treatment with estradiol, ERalpha is still present on the CYP1A1 promoter but no longer at pS2. RNA interference studies with T47D cells support a role for ERalpha in TCDD-dependent CYP1A1 expression. Our data suggest that ERalpha acts as a coregulator of AhR-mediated transcriptional activation and that the recruitment of ERalpha by AhR represents a novel mechanism AhR-ERalpha cross talk.
Figures






Similar articles
-
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor interacts with estrogen receptor alpha and orphan receptors COUP-TFI and ERRalpha1.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2000 Jan 1;373(1):163-74. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1999.1552. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2000. PMID: 10620335
-
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor modulation of estrogen receptor α-mediated gene regulation by a multimeric chromatin complex involving the two receptors and the coregulator RIP140.Toxicol Sci. 2012 Feb;125(2):401-11. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfr300. Epub 2011 Nov 9. Toxicol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22071320 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen receptor subtype- and promoter-specific modulation of aryl hydrocarbon receptor-dependent transcription.Mol Cancer Res. 2009 Jun;7(6):977-86. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-08-0396. Epub 2009 May 26. Mol Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19470599
-
Role of coactivators in transcriptional activation by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2005 Jan 15;433(2):379-86. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2004.09.031. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2005. PMID: 15581594 Review.
-
Mechanisms of inhibitory aryl hydrocarbon receptor-estrogen receptor crosstalk in human breast cancer cells.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2000 Jul;5(3):295-306. doi: 10.1023/a:1009550912337. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2000. PMID: 14973392 Review.
Cited by
-
Exactly the same but different: promiscuity and diversity in the molecular mechanisms of action of the aryl hydrocarbon (dioxin) receptor.Toxicol Sci. 2011 Nov;124(1):1-22. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfr218. Epub 2011 Sep 9. Toxicol Sci. 2011. PMID: 21908767 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The serine-threonine protein kinase PAK4 is dispensable in zebrafish: identification of a morpholino-generated pseudophenotype.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 19;9(6):e100268. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100268. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24945275 Free PMC article.
-
Dioxin-like PCBs and endometriosis.Syst Biol Reprod Med. 2010 Apr;56(2):132-46. doi: 10.3109/19396360903381023. Syst Biol Reprod Med. 2010. PMID: 20377312 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signaling network map of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor.J Cell Commun Signal. 2016 Dec;10(4):341-346. doi: 10.1007/s12079-016-0341-y. Epub 2016 Jul 27. J Cell Commun Signal. 2016. PMID: 27465749 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Comparative metabolomic and genomic analyses of TCDD-elicited metabolic disruption in mouse and rat liver.Toxicol Sci. 2012 Jan;125(1):41-55. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfr262. Epub 2011 Sep 29. Toxicol Sci. 2012. PMID: 21964420 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barkhem, T., B. Carlsson, Y. Nilsson, E. Enmark, J.-Å. Gustafsson, and S. Nilsson. 1998. Differential response of estrogen receptor alpha and estrogen receptor beta to partial estrogen agonists/antagonists. Mol. Pharmacol. 54:105-112. - PubMed
-
- Beischlag, T. V., S. Wang, D. W. Rose, J. Torchia, S. Reisz-Porszasz, K. Muhammad, W. E. Nelson, M. R. Probst, M. G. Rosenfeld, and O. Hankinson. 2002. Recruitment of the NCoA/SRC-1/p160 family of transcriptional coactivators by the aryl hydrocarbon receptor/aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator complex. Mol. Cell. Biol. 22:4319-4333. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carver, L. A., and C. A. Bradfield. 1997. Ligand-dependent interaction of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor with a novel immunophilin homolog in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 272:11452-11456. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
