Inhibition of MuSK expression by CREB interacting with a CRE-like element and MyoD
- PMID: 15964791
- PMCID: PMC1156998
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.13.5329-5338.2005
Inhibition of MuSK expression by CREB interacting with a CRE-like element and MyoD
Abstract
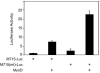
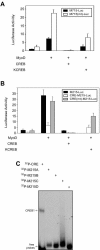
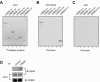
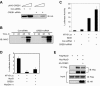
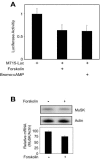
The type I receptor-like protein tyrosine kinase MuSK is essential for the neuromuscular junction formation. MuSK expression is tightly regulated during development, but the underlying mechanisms were unclear. Here we identified a novel mechanism by which MuSK expression may be regulated. A cyclic AMP response element (CRE)-like element in the 5'-flanking region of the MuSK gene binds to CREB1 (CRE-binding protein 1). Mutation of this element increases the MuSK promoter activity, suggesting a role for CREB1 in attenuation of MuSK expression. Interestingly, CREB mutants unable to bind to DNA also inhibit MuSK promoter activity, suggesting a CRE-independent inhibitory mechanism. In agreement, CREB1 could inhibit a mutant MuSK transgene reporter whose CRE site was mutated. We provide evidence that CREB interacts directly with MyoD, a myogenic factor essential for MuSK expression in muscle cells. Suppression of CREB expression by small interfering RNA increases MuSK promoter activity. These results demonstrate an important role for CREB1 in the regulation of MuSK expression.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Role of basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) and CREB transcription factors in the regulation of Sertoli cell androgen-binding protein expression.Mol Reprod Dev. 2004 Jul;68(3):269-78. doi: 10.1002/mrd.20080. Mol Reprod Dev. 2004. PMID: 15112319
-
Regulation of niemann-pick c1 gene expression by the 3'5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate pathway in steroidogenic cells.Mol Endocrinol. 2003 Apr;17(4):704-15. doi: 10.1210/me.2002-0093. Epub 2003 Jan 16. Mol Endocrinol. 2003. PMID: 12554781
-
Role of basic region leucine zipper transcription factors cyclic AMP response element binding protein (CREB), CREB2, activating transcription factor 2 and CAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha in cyclic AMP response element-mediated transcription.J Neurochem. 2005 Jan;92(2):321-36. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02882.x. J Neurochem. 2005. PMID: 15663480
-
Synergistic signaling by corticotropin-releasing hormone and leukemia inhibitory factor bridged by phosphorylated 3',5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element binding protein at the Nur response element (NurRE)-signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT) element of the proopiomelanocortin promoter.Mol Endocrinol. 2004 Dec;18(12):2997-3010. doi: 10.1210/me.2003-0417. Epub 2004 Aug 19. Mol Endocrinol. 2004. PMID: 15319449
-
Regulation of steroidogenesis and the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein by a member of the cAMP response-element binding protein family.Mol Endocrinol. 2002 Jan;16(1):184-99. doi: 10.1210/mend.16.1.0759. Mol Endocrinol. 2002. PMID: 11773448
Cited by
-
Slit2 as a β-catenin/Ctnnb1-dependent retrograde signal for presynaptic differentiation.Elife. 2015 Jul 10;4:e07266. doi: 10.7554/eLife.07266. Elife. 2015. PMID: 26159615 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the promoter region of the bovine SIX1 gene: Roles of MyoD, PAX7, CREB and MyoG.Sci Rep. 2017 Oct 3;7(1):12599. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-12787-5. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28974698 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription Regulation of Tceal7 by the Triple Complex of Mef2c, Creb1 and Myod.Biology (Basel). 2022 Mar 16;11(3):446. doi: 10.3390/biology11030446. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35336819 Free PMC article.
-
cAMP responsive element binding protein-1 is a transcription factor of lysosomal-associated protein transmembrane-4 Beta in human breast cancer cells.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e57520. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057520. Epub 2013 Feb 28. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23469012 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of CREB and bHLH transcriptional signaling pathways through direct heterodimerization of the proteins: role in muscle and testis development.Mol Reprod Dev. 2008 Nov;75(11):1637-52. doi: 10.1002/mrd.20902. Mol Reprod Dev. 2008. PMID: 18361414 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arber, S., G. Halder, and P. Caroni. 1994. Muscle LIM protein, a novel essential regulator of myogenesis, promotes myogenic differentiation. Cell 79:221-231. - PubMed
-
- Bailey, P., M. Downes, P. Lau, J. Harris, S. L. Chen, Y. Hamamori, V. Sartorelli, and G. E. Muscat. 1999. The nuclear receptor corepressor N-CoR regulates differentiation: N-CoR directly interacts with MyoD. Mol. Endocrinol. 13:1155-1168. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
