The Saccharomyces cerevisiae Piccolo NuA4 histone acetyltransferase complex requires the Enhancer of Polycomb A domain and chromodomain to acetylate nucleosomes
- PMID: 15964809
- PMCID: PMC1156996
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.13.5535-5542.2005
The Saccharomyces cerevisiae Piccolo NuA4 histone acetyltransferase complex requires the Enhancer of Polycomb A domain and chromodomain to acetylate nucleosomes
Abstract
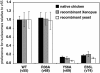
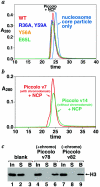
Chromatin modification complexes are key gene regulatory factors which posttranslationally modify the histone component of chromatin with epigenetic marks. To address what features of chromatin modification complexes are responsible for the specific recognition of nucleosomes compared to naked histones, we have performed a functional dissection of the Esa1-containing Saccharomyces cerevisiae Piccolo NuA4 histone acetyltransferase complex. Our studies define the Piccolo determinants sufficient to assemble its three subunits into a complex as well as Piccolo determinants sufficient to specifically acetylate a chromatin template. We find that the conserved Enhancer of Polycomb A (EPcA) homology region of the Epl1 component and the N-terminal 165 amino acids of the Yng2 component of Piccolo are sufficient with Esa1 to specifically act on nucleosomes. We also find that the Esa1 chromodomain plays a critical role in Piccolo's ability to distinguish between histones and nucleosomes. In particular, specific point mutations in the chromodomain putative hydrophobic cage which strongly hinder growth in yeast greatly reduce histone acetyltransferase activity on nucleosome substrates, independent of histone methylation or other modifications. However, the chromodomain is not required for Piccolo to bind to nucleosomes, suggesting a role for the chromodomain in a catalysis step after nucleosome binding.
Figures



References
-
- Akhtar, A., D. Zink, and P. B. Becker. 2000. Chromodomains are protein-RNA interaction modules. Nature 407:405-409. - PubMed
-
- Balasubramanian, R., M. G. Pray-Grant, W. Selleck, P. A. Grant, and S. Tan. 2002. Role of the Ada2 and Ada3 transcriptional coactivators in histone acetylation. J. Biol. Chem. 277:7989-7995. - PubMed
-
- Becker, P. B., and W. Horz. 2002. ATP-dependent nucleosome remodeling. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 71:247-273. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
