Arginine methylation provides epigenetic transcription memory for retinoid-induced differentiation in myeloid cells
- PMID: 15964820
- PMCID: PMC1156990
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.13.5648-5663.2005
Arginine methylation provides epigenetic transcription memory for retinoid-induced differentiation in myeloid cells
Abstract
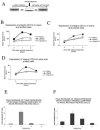
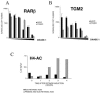
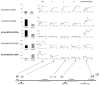
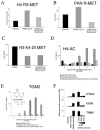
Cellular differentiation is governed by changes in gene expression, but at the same time, a cell's identity needs to be maintained through multiple cell divisions during maturation. In myeloid cell lines, retinoids induce gene expression and a well-characterized two-step lineage-specific differentiation. To identify mechanisms that contribute to cellular transcriptional memory, we analyzed the epigenetic changes taking place on regulatory regions of tissue transglutaminase, a gene whose expression is tightly linked to retinoid-induced differentiation. Here we report that the induction of an intermediary or "primed" state of myeloid differentiation is associated with increased H4 arginine 3 and decreased H3 lysine 4 methylation. These modifications occur before transcription and appear to prime the chromatin for subsequent hormone-regulated transcription. Moreover, inhibition of methyltransferase activity, pre-acetylation, or activation of the enzyme PAD4 attenuated retinoid-regulated gene expression, while overexpression of PRMT1, a methyltransferase, enhanced retinoid responsiveness. Taken together, our results suggest that H4 arginine 3 methylation is a bona fide positive epigenetic marker and regulator of transcriptional responsiveness as well as a signal integration mechanism during cell differentiation and, as such, may provide epigenetic memory.
Figures





References
-
- Agalioti, T., G. Chen, and D. Thanos. 2002. Deciphering the transcriptional histone acetylation code for a human gene. Cell 111:381-392. - PubMed
-
- An, W., J. Kim, and R. G. Roeder. 2004. Ordered cooperative functions of PRMT1, p300, and CARM1 in transcriptional activation by p53. Cell 117:735-748. - PubMed
-
- Benko, S., J. D. Love, M. Beladi, J. W. Schwabe, and L. Nagy. 2003. Molecular determinants of the balance between co-repressor and co-activator recruitment to the retinoic acid receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 278:43797-43806. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein, B. E., M. Kamal, K. Lindblad-Toh, S. Bekiranov, D. K. Bailey, D. J. Huebert, S. McMahon, E. K. Karlsson, E. J. Kulbokas III, T. R. Gingeras, S. L. Schreiber, and E. S. Lander. 2005. Genomic maps and comparative analysis of histone modifications in human and mouse. Cell 120:169-181. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
