Nitric oxide increases carbon monoxide production by piglet cerebral microvessels
- PMID: 15964921
- PMCID: PMC1315289
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00464.2005
Nitric oxide increases carbon monoxide production by piglet cerebral microvessels
Abstract
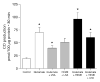
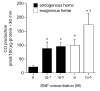
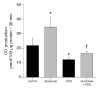
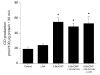
Carbon monoxide (CO) and nitric oxide (NO) can be involved in the regulation of cerebral circulation. Inhibition of production of either one of these gaseous intercellular messengers inhibits newborn pig cerebral arteriolar dilation to the excitatory amino acid glutamate. Glutamate can increase NO production. Therefore, the present study tests the hypothesis that NO, which is increased by glutamate, stimulates the production of CO by cerebral microvessels. Experiments used freshly isolated cerebral microvessels from piglets that express only heme oxygenase-2 (HO-2). CO production was measured by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Although inhibition of nitric oxide synthase (NOS) with N(omega)-nitro-l-arginine (l-NNA) did not alter basal HO-2 catalytic activity or CO production, l-NNA blocked glutamate stimulation of HO-2 activity and CO production. Furthermore, the NO donor sodium nitroprusside mimicked the actions of glutamate on HO-2 and CO production. The action of NO appears to be via cGMP because 8-bromo-cGMP mimics and 1H-[1,2,4]oxadiazole-[4,3-a]quinoxalin-1-one (ODQ) blocks glutamate stimulation of CO production and HO-2 catalytic activity. Inhibitors of neither casein kinase nor phosphotidylinositol 3-kinase altered HO-2 catalytic activity. Conversely, inhibition of calmodulin with calmidazolium chloride blocked glutamate stimulation of CO production and reduced HO-2 catalytic activity. These data suggest that glutamate may activate NOS producing NO that leads to CO synthesis via a cGMP-dependent elevation of HO-2 catalytic activity. These results are consistent with the findings in vivo that either HO or NOS inhibition blocks cerebrovascular dilation to glutamate in piglets.
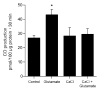
Figures

Similar articles
-
The permissive role of endothelial NO in CO-induced cerebrovascular dilation.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2004 Oct;287(4):H1459-65. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00369.2004. Epub 2004 Jun 10. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15191891
-
Interaction between endogenously produced carbon monoxide and nitric oxide in regulation of renal afferent arterioles.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2006 Dec;291(6):H2772-8. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00528.2006. Epub 2006 Jul 14. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16844915
-
Role of cGMP in carbon monoxide-induced cerebral vasodilation in piglets.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2004 Jan;286(1):H304-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00810.2003. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2004. PMID: 14684363
-
Carbon monoxide as an endogenous vascular modulator.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011 Jul;301(1):H1-H11. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00230.2011. Epub 2011 Apr 15. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21498777 Free PMC article. Review.
-
No nitric oxide for HO-1 from sodium nitroprusside.Mol Pharmacol. 2006 May;69(5):1507-9. doi: 10.1124/mol.106.023416. Epub 2006 Feb 13. Mol Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16476785 Review.
Cited by
-
Carbon monoxide and Ca2+-activated K+ channels in cerebral arteriolar responses to glutamate and hypoxia in newborn pigs.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007 Nov;293(5):H3193-200. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00274.2007. Epub 2007 Aug 31. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17766483 Free PMC article.
-
Glutamate-induced calcium signals stimulate CO production in piglet astrocytes.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011 Aug;301(2):H428-33. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.01277.2010. Epub 2011 May 13. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21572018 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms involved in the cerebrovascular dilator effects of cortical spreading depression.Prog Neurobiol. 2008 Dec 11;86(4):379-95. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2008.09.008. Epub 2008 Sep 12. Prog Neurobiol. 2008. PMID: 18835324 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AICAR preconditioning prevents postischemic leukocyte rolling and adhesion: role of K(ATP) channels and heme oxygenase.Microcirculation. 2009 Feb;16(2):167-76. doi: 10.1080/10739680802355897. Microcirculation. 2009. PMID: 19152177 Free PMC article.
-
Carbon monoxide: a critical quantitative analysis and review of the extent and limitations of its second messenger function.Clin Pharmacol. 2015 Feb 26;7:37-56. doi: 10.2147/CPAA.S79626. eCollection 2015. Clin Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25750547 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Boehning D, Moon C, Sharma S, Hurt KJ, Hester LD, Ronnett GV, Shugar D, Snyder SS. Carbon monoxide neurotransmission activated by CK2 phosphorylation of heme oxygenase-2. Neuron. 2003;40:129–137. - PubMed
-
- Boehning D, Sedaghat L, Sedlak TW, Snyder SS. Heme oxygenase-2 is activated by calcium-calmodulin. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:30927–30930. - PubMed
-
- Boehning D, Snyder SH. Novel neural modulators. Ann Rev Neurosci. 2003;26:105–131. - PubMed
-
- Canzoniero LM, Sensi SL, Turetsky DM, Finley MF, Choi DW, Huettner JE. Glutamate receptor-mediated calcium entry in neurons derived from P19 embryonal carcinoma cells. J Neurosci Res. 1996;45:226–36. - PubMed
-
- Ding Y, McCoubrey WK, Jr, Maines MD. Interaction of heme oxygenase-2 with nitric oxide donors. Is the oxygenase an intracellular ‘sink’ for NO? Eur J Biochem. 1999;264:854–861. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

