Altering cannabinoid signaling during development disrupts neuronal activity
- PMID: 15964987
- PMCID: PMC1166590
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0409641102
Altering cannabinoid signaling during development disrupts neuronal activity
Abstract
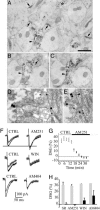
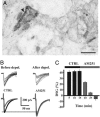
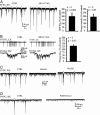
In adult cortical tissue, recruitment of GABAergic inhibition prevents the progression of synchronous population discharges to epileptic activity. However, at early developmental stages, GABA is excitatory and thus unable to fulfill this role. Here, we report that retrograde signaling involving endocannabinoids is responsible for the homeostatic control of synaptic transmission and the resulting network patterns in the immature hippocampus. Blockade of cannabinoid type 1 (CB1) receptor led to epileptic discharges, whereas overactivation of CB1 reduced network activity in vivo. Endocannabinoid signaling thus is able to keep population discharge patterns within a narrow physiological time window, balancing between epilepsy on one side and sparse activity on the other, which may result in impaired developmental plasticity. Disturbing this delicate balance during pregnancy in either direction, e.g., with marijuana as a CB1 agonist or with an antagonist marketed as an antiobesity drug, can have profound consequences for brain maturation even in human embryos.
Figures


Comment in
-
Endocannabinoids: a critical regulator of activity in the developing brain.Epilepsy Curr. 2006 Jan-Feb;6(1):18-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1535-7511.2005.00082.x. Epilepsy Curr. 2006. PMID: 16477318 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Wang, H., Guo, Y., Wang, D., Kingsley, P. J., Marnett, L. J., Das, S. K., DuBois, R. N. & Dey, S. K. (2004) Nat. Med. 10, 1074-1080. - PubMed
-
- Fergusson, D. M., Horwood, L. J. & Northstone, K. (2002) Br. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 109, 21-27. - PubMed
-
- Fried, P. A., Watkinson, B. & Gray, R. (2003) Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 25, 427-436. - PubMed
-
- Wilson, R. I. & Nicoll, R. A. (2001) Nature 410, 588-592. - PubMed
-
- Freund, T. F., Katona, I. & Piomelli, D. (2003) Physiol Rev. 83, 1017-1066. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

