Reversible posterior leucoencephalopathy syndrome: a cause of temporary cortical blindness
- PMID: 15965184
- PMCID: PMC1772723
- DOI: 10.1136/bjo.2004.060400
Reversible posterior leucoencephalopathy syndrome: a cause of temporary cortical blindness
Figures
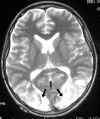
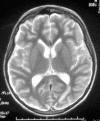
References
-
- Hinchey J, Chaves C, Appignani B, et al. A reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome. N Engl J Med 1996;334:494–500. - PubMed
-
- Pavlakis SG, Frank Y, Chusid R. Hypertensive encephalopathy, reversible occipitoparietal encephalopathy, or reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy: three names for an old syndrome. J Child Neurol 1999;14:277–81. - PubMed
-
- Suminoe A, Matsuzaki A, Kira R, et al. Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome in children with cancers. J Paed Haem Oncol 2003;25:236–9. - PubMed
-
- Singhi P, Subramanian C, Jain V, et al. Reversible brain lesions in childhood hypertension. Acta Paediatr 2002;91:1005–7. - PubMed
-
- Gay CT, Bodensteiner JB, Nitschke R, et al. Reversible treatment-related leukoencephalopathy. J Child Neurol 1989;4:208–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
