Molecular genetic analysis of the nested Drosophila melanogaster lamin C gene
- PMID: 15965247
- PMCID: PMC1456510
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.105.043208
Molecular genetic analysis of the nested Drosophila melanogaster lamin C gene
Abstract
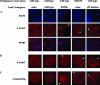
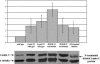
Lamins are intermediate filaments that line the inner surface of the nuclear envelope, providing structural support and making contacts with chromatin. There are two types of lamins, A- and B-types, which differ in structure and expression. Drosophila possesses both lamin types, encoded by the LamC (A-type) and lamin Dm0 (B-type) genes. LamC is nested within an intron of the essential gene ttv. We demonstrate that null mutations in LamC are lethal, and expression of a wild-type LamC transgene rescues lethality of LamC but not ttv mutants. Mutations in the human A-type lamin gene lead to diseases called laminopathies. To determine if Drosophila might serve as a useful model to study lamin biology and disease mechanisms, we generated transgenic flies expressing mutant LamC proteins modeled after human disease-causing lamins. These transgenic animals display a nuclear lamin aggregation phenotype remarkably similar to that observed when human mutant A-type lamins are expressed in mammalian cells. LamC aggregates also cause disorganization of lamin Dm0, indicating interdependence of both lamin types for proper lamina assembly. Taken together, these data provide the first detailed genetic analysis of the LamC gene and support using Drosophila as a model to study the role of lamins in disease.
Figures




References
-
- Adams, M. D., and J. J. Sekelsky, 2002. From sequence to phenotype: reverse genetics in Drosophila melanogaster. Nat. Rev. Genet. 3: 189–198. - PubMed
-
- Arimura, T., A. Helbling-Leclerc, C. Massart, S. Varnous, F. Niel et al., 2005. Mouse model carrying H222P-Lmna mutation develops muscular dystrophy and dilated cardiomyopathy similar to human striated muscle laminopathies. Hum. Mol. Genet. 14: 155–169. - PubMed
-
- Ashburner, M., 1989. Drosophila: A Laboratory Handbook. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
-
- Bellaiche, Y., I. The and N. Perrimon, 1998. Tout-velu is a Drosophila homologue of the putative tumour suppressor EXT-1 and is needed for Hh diffusion. Nature 394: 85–88. - PubMed
-
- Bender, W., P. Spierer and D. S. Hogness, 1983. Chromosomal walking and jumping to isolate DNA from the Ace and rosy loci and the bithorax complex in Drosophila melanogaster. J. Mol. Biol. 168: 17–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

