The Drosophila meiotic mutant mei-352 is an allele of klp3A and reveals a role for a kinesin-like protein in crossover distribution
- PMID: 15965253
- PMCID: PMC1449747
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.105.041194
The Drosophila meiotic mutant mei-352 is an allele of klp3A and reveals a role for a kinesin-like protein in crossover distribution
Abstract
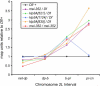
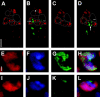
The semisterile meiotic mutant mei-352 alters the distribution of meiotic exchanges without greatly affecting their total frequency. We show that the mei-352 mutation is an allele of the klp3A gene, which encodes a kinesin-like protein of the Kinesin-4 family. The semisterility observed in mei-352 females results from a known defect of klp3A oocytes in mediating pronuclear fusion. Interestingly, other klp3A alleles also exhibit defects in meiotic recombination similar to those of mei-352. Finally, we show that the Klp3A protein localizes within the oocyte nucleus during meiotic prophase, the time at which exchange distribution is established, and extensively colocalizes with DNA. The parallel of the klp3A phenotype with a meiotic defect observed for kar3 mutants in yeast suggests a role for kinesins in early meiosis and might reflect a previously suggested role for this class of kinesins in chromosome condensation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Loss of Drosophila Mei-41/ATR Alters Meiotic Crossover Patterning.Genetics. 2018 Feb;208(2):579-588. doi: 10.1534/genetics.117.300634. Epub 2017 Dec 15. Genetics. 2018. PMID: 29247012 Free PMC article.
-
The Drosophila kinesin-like protein KLP3A is required for proper behavior of male and female pronuclei at fertilization.Development. 1997 Jun;124(12):2365-76. doi: 10.1242/dev.124.12.2365. Development. 1997. PMID: 9199363
-
Drosophila ERCC1 is required for a subset of MEI-9-dependent meiotic crossovers.Genetics. 2005 Aug;170(4):1737-45. doi: 10.1534/genetics.104.036178. Epub 2005 Jun 8. Genetics. 2005. PMID: 15944364 Free PMC article.
-
Meiotic chromosome distribution in Drosophila oocytes: roles of two kinesin-related proteins.Chromosoma. 1992 Dec;102(1):1-8. doi: 10.1007/BF00352283. Chromosoma. 1992. PMID: 1291224 Review.
-
Meiosis in Drosophila: seeing is believing.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Nov 7;92(23):10443-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.23.10443. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995. PMID: 7479817 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The chromokinesin Klp3a and microtubules facilitate acentric chromosome segregation.J Cell Biol. 2017 Jun 5;216(6):1597-1608. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201604079. Epub 2017 May 12. J Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28500183 Free PMC article.
-
The passing of the last oracle: Adelaide Carpenter and Drosophila meiosis.Chromosoma. 2024 Oct;133(4):247-251. doi: 10.1007/s00412-024-00825-x. Chromosoma. 2024. PMID: 39325143 No abstract available.
-
The formation of the central element of the synaptonemal complex may occur by multiple mechanisms: the roles of the N- and C-terminal domains of the Drosophila C(3)G protein in mediating synapsis and recombination.Genetics. 2007 Dec;177(4):2445-56. doi: 10.1534/genetics.107.078717. Epub 2007 Oct 18. Genetics. 2007. PMID: 17947423 Free PMC article.
-
Astral microtubule cross-linking safeguards uniform nuclear distribution in the Drosophila syncytium.J Cell Biol. 2022 Jan 3;221(1):e202007209. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202007209. Epub 2021 Nov 12. J Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 34766978 Free PMC article.
-
Corona is required for higher-order assembly of transverse filaments into full-length synaptonemal complex in Drosophila oocytes.PLoS Genet. 2008 Sep 19;4(9):e1000194. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000194. PLoS Genet. 2008. PMID: 18802461 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baker, B. S., and J. C. Hall, 1976 Meiotic mutants: genetic control of meiotic recombination and chromosome segregation, pp. 351–434 in The Genetics and Biology of Drosophila, Vol. 1a, edited by M. Ashburner and E. Novitski. Academic Press, New York.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

