M(2) and M(3) muscarinic receptor-mediated contractions in longitudinal smooth muscle of the ileum studied with receptor knockout mice
- PMID: 15965495
- PMCID: PMC1576249
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706300
M(2) and M(3) muscarinic receptor-mediated contractions in longitudinal smooth muscle of the ileum studied with receptor knockout mice
Abstract
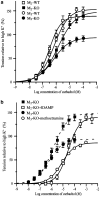
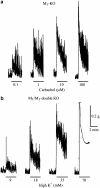
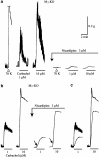
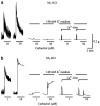
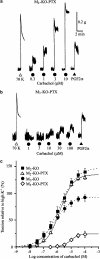
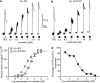
Isometric contractile responses to carbachol were studied in ileal longitudinal smooth muscle strips from wild-type mice and mice genetically lacking M(2) or M(3) muscarinic receptors, in order to characterize the mechanisms involved in M(2) and M(3) receptor-mediated contractile responses. Single applications of carbachol (0.1-100 microM) produced concentration-dependent contractions in preparations from M(2)-knockout (KO) and M(3)-KO mice, mediated via M(3) and M(2) receptors, respectively, as judged by the sensitivity of contractile responses to blockade by the M(2)-preferring antagonist methoctramine (300 nM) or the M(3)-preferring antagonist 4-DAMP (30 nM). The M(2)-mediated contractions were mimicked in shape by submaximal stimulation with high K(+) concentrations (up to 35 mM), almost abolished by voltage-dependent Ca(2+) channel (VDCC) antagonists or depolarization with 140 mM K(+) medium, and greatly reduced by pertussis toxin (PTX) treatment. The M(3)-mediated contractions were only partially inhibited by VDCC antagonists or 140 mM K(+)-depolarization medium, and remained unaffected by PTX treatment. The contractions observed during high K(+) depolarization consisted of different components, either sensitive or insensitive to extracellular Ca(2+). The carbachol contractions observed with wild-type preparations consisted of PTX-sensitive and -insensitive components. The PTX-sensitive component was functionally significant only at low carbachol concentrations. The results suggest that the M(2) receptor, through PTX-sensitive mechanisms, induces ileal contractions that depend on voltage-dependent Ca(2+) entry, especially associated with action potential discharge, and that the M(3) receptor, through PTX-insensitive mechanisms, induces contractions that depend on voltage-dependent and -independent Ca(2+) entry and intracellular Ca(2+) release. In intact tissues coexpressing M(2) and M(3) receptors, M(2) receptor activity appears functionally relevant only when fractional receptor occupation is relatively small.
Figures
References
-
- BOLTON T.B. Mechanisms of action of transmitters and other substances on smooth muscle. Physiol. Rev. 1979;59:647–671. - PubMed
-
- BOLTON T.B., ZHOLOS A.V. Activation of M2 muscarinic receptors in guinea-pig ileum opens cationic channels modulated by M3 muscarinic receptors. Life Sci. 1997;60:1121–1128. - PubMed
-
- CANDELL L.M., YUN S.H., TRAN L.L, EHLERT F.J. Differential coupling of subtypes of the muscarinic receptor to adenylate cyclase and phosphoinositide hydrolysis in the longitudinal muscle of the rat ileum. Mol. Pharmacol. 1990;38:689–697. - PubMed
-
- EGLEN R.M., HEGDE S.S., WATSON N. Muscarinic receptor subtypes and smooth muscle function. Pharmacol. Rev. 1996;48:531–565. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

