Modulation of voltage-dependent Ba2+ currents in the guinea-pig gastric antrum by cyclic nucleotide-dependent pathways
- PMID: 15965497
- PMCID: PMC1576245
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706295
Modulation of voltage-dependent Ba2+ currents in the guinea-pig gastric antrum by cyclic nucleotide-dependent pathways
Abstract
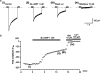
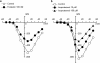
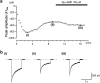
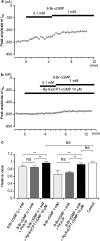
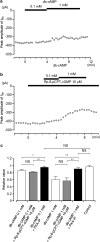
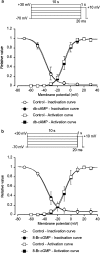
We have investigated whether the activation of cAMP- and cGMP-dependent pathways modifies the properties of voltage-dependent Ba(2+) currents (I(Ba)) recorded from guinea-pig gastric myocytes using patch-clamp techniques. All experiments were carried on single smooth muscle cells, dispersed from the circular layer of the guinea-pig gastric antrum. Both dibutyryl cAMP (db-cAMP, 0.1-1 mM), a membrane-permeable ester of cAMP, and isoproterenol, a selective beta-stimulant, inhibited I(Ba) in a concentration-dependent manner. Forskolin, but not dideoxy-forskolin, an inactive isomer of forskolin, inhibited the peak amplitude of I(Ba). In the presence of either Rp-cAMP or the PKA (cAMP-dependent protein kinase) inhibitor peptide 5-24 (PKA-IP), neither forskolin nor db-cAMP inhibited I(Ba). After establishing a conventional whole-cell recording, the peak amplitude of I(Ba) gradually decreased when the catalytic subunit of PKA was included in the pipette. The further application of Rp-cAMP reversibly enhanced I(Ba). Sodium nitroprusside (0.1-1 mM) and 8-Br-cGMP (0.1-1 mM) also inhibited I(Ba) in a concentration-dependent manner. The inhibitory effects of forskolin or db-cAMP on I(Ba) were not significantly changed by pretreatment with a cGMP-dependent protein kinase (PKG) inhibitor. Similarly, the inhibitory actions of 8-Br-cGMP on I(Ba) were not modified by PKA-IP. The membrane-permeable cyclic nucleotides db-cAMP and 8-Br-cGMP caused little shift of the voltage dependence of the steady-state inactivation and reactivation curves. Neither of the membrane-permeable cyclic nucleotides db-cAMP or 8-Br-cGMP had additive inhibitory effects on I(Ba). These results indicate that two distinct cyclic nucleotide-dependent pathways are present in the guinea-pig gastric antrum, and that both inhibited I(Ba) in an independent manner.
Figures


References
-
- BUNEMANN M., GERHARDSTEIN B.L., GAO T., HOSEY M.M. Functional regulation of L-type calcium channels via protein kinase A-mediated phosphorylation of the β2 subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:33851–33854. - PubMed
-
- BÜLBRING E., TOMITA T. Catecholamine action on smooth muscle. Pharmacol. Rev. 1987;39:49–96. - PubMed
-
- DAVILA H.M. Molecular and functional diversity of voltage-gated calcium channels. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 1999;868:102–117. - PubMed
-
- FARRUGIA G. Ionic conductances in gastrointestinal smooth muscles and interstitial cells of Cajal. Ann. Rev. Physiol. 1999;61:45–84. - PubMed
-
- FURNESS J.B., COSTA M. The Enteric Nervous System. Edinburgh: Churchill-Livingstone; 1987.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

