Chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells induce changes in gene expression of CD4 and CD8 T cells
- PMID: 15965501
- PMCID: PMC1150284
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI24176
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells induce changes in gene expression of CD4 and CD8 T cells
Abstract
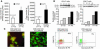
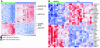
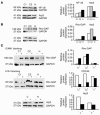
To examine the impact of tumors on the immune system, we compared global gene expression profiles of peripheral blood T cells from previously untreated patients with B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) with those from age-matched healthy donors. Although the cells analyzed were not part of the malignant clone, analysis revealed differentially expressed genes, mainly involved in cell differentiation in CD4 cells and defects in cytoskeleton formation, vesicle trafficking, and cytotoxicity in CD8 cells of the CLL patients. In coculture experiments using CLL cells and T cells from healthy allogeneic donors, similar defects developed in both CD4 and CD8 cells. These changes were induced only with direct contact and were not cytokine mediated. Identification of the specific pathways perturbed in the T cells of cancer-bearing patients will allow us to assess steps to repair these defects, which will likely be required to enhance antitumor immunity.
Figures


References
-
- Benjamin D, Knobloch TJ, Dayton MA. Human B-cell interleukin-10: B-cell lines derived from patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and Burkitt’s lymphoma constitutively secrete large quantities of interleukin-10. Blood. 1992;80:1289–1298. - PubMed
-
- Benjamin D, Park CD, Sharma V. Human B cell interleukin 10. Leuk. Lymphoma. 1994;12:205–210. - PubMed
-
- Fayad L, et al. Interleukin-6 and interleukin-10 levels in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: correlation with phenotypic characteristics and outcome. Blood. 2001;97:256–263. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

