Selective suppression of in vivo tumorigenicity by semaphorin SEMA3F in lung cancer cells
- PMID: 15967098
- PMCID: PMC1501157
- DOI: 10.1593/neo.04721
Selective suppression of in vivo tumorigenicity by semaphorin SEMA3F in lung cancer cells
Abstract
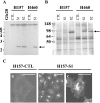
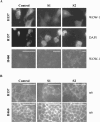
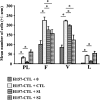
Loss of the 3p21.3-encoded semaphorins, SEMA3B and SEMA3F, is implicated in lung cancer development. Although both antagonize VEGF binding/response to neuropilin (NRP) receptors, in lung cancer lines, SEMA3F is predominantly expressed and preferentially utilizes NRP2. In lung cancer patients, SEMA3F loss correlates with advanced disease and increased VEGF binding to tumor cells. In cell lines, VEGF enhances adhesion and migration in an integrin-dependent manner, and exogenous SEMA3F causes cells to round and lose extracellular contacts. Using retroviral infections, we established stable SEMA3F transfectants in two NSCLC cell lines, NCI-H157 and NCI-H460. When orthotopically injected into nude rats, both control lines caused lethal tumors in all recipients. In contrast, all animals receiving H157-SEMA3F cells, survived to 100 days, whereas all H157 controls succumbed. In H460 cells, which express NRP1 but not NRP2, SEMA3F did not prolong survival. This antitumor effect in H157 cells was associated with loss of activated alpha(v)beta(3) integrin and adhesion to extracellular matrix components. In addition, H157-SEMA3F cells, and parental H157 cells exposed to SEMA3F-conditioned medium, showed loss of p42/p44 MAPK phosphorylation. Thus, in this in vivo lung cancer model, SEMA3F has potent antitumor effects, which may impinge on activated integrin and MAPK signaling.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Semaphorin SEMA3F affects multiple signaling pathways in lung cancer cells.Cancer Res. 2007 Sep 15;67(18):8708-15. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3612. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17875711
-
Semaphorin 3F, a chemorepulsant for endothelial cells, induces a poorly vascularized, encapsulated, nonmetastatic tumor phenotype.J Clin Invest. 2004 Nov;114(9):1260-71. doi: 10.1172/JCI21378. J Clin Invest. 2004. PMID: 15520858 Free PMC article.
-
Semaphorin SEMA3F has a repulsing activity on breast cancer cells and inhibits E-cadherin-mediated cell adhesion.Neoplasia. 2005 Feb;7(2):180-9. doi: 10.1593/neo.04481. Neoplasia. 2005. PMID: 15802023 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropilin and its ligands in normal lung and cancer.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2002;515:103-14. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-0119-0_9. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2002. PMID: 12613547 Review.
-
Neuropilins in neoplasms: expression, regulation, and function.Exp Cell Res. 2006 Mar 10;312(5):584-93. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2005.11.024. Epub 2006 Jan 27. Exp Cell Res. 2006. PMID: 16445911 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibitory effects of Semaphorin 3F as an alternative candidate to anti-VEGF monoclonal antibody on angiogenesis.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2019 Oct;55(9):756-765. doi: 10.1007/s11626-019-00392-x. Epub 2019 Aug 16. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2019. PMID: 31420803
-
The role of the semaphorins in cancer.Cell Adh Migr. 2016 Nov;10(6):652-674. doi: 10.1080/19336918.2016.1197478. Epub 2016 Aug 17. Cell Adh Migr. 2016. PMID: 27533782 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review of the past, present, and future directions of neoplasia.Neoplasia. 2005 Dec;7(12):1039-46. doi: 10.1593/neo.05793. Neoplasia. 2005. PMID: 16354585 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Semaphorin, neuropilin and VEGF expression in glial tumours: SEMA3G, a prognostic marker?Br J Cancer. 2008 Oct 7;99(7):1153-60. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6604641. Epub 2008 Sep 9. Br J Cancer. 2008. PMID: 18781179 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of E-cadherin in lung cancer and interaction with growth suppression by histone deacetylase inhibition.J Thorac Oncol. 2009 Dec;4(12):1455-65. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181bc9419. J Thorac Oncol. 2009. PMID: 20009910 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Semaphorin Nomenclature Committee, author. Unified nomenclature for the semaphorins/collapsins. Cell. 1999;97:551–552. - PubMed
-
- Luo Y, Raible D, Raper A. Collapsin: a protein in brain that induces the collapse and paralysis of neuronal growth cones. Cell. 1993;75:217–227. - PubMed
-
- Kolodkin A, Matthes D, Goodman C. The semaphorin genes encode a family of transmembrane and secreted growth cone guidance molecules. Cell. 1993;75:1389–1399. - PubMed
-
- Kolodkin A, Levengood D, Rowe E, Tai Y, Giger R, Ginty D. Neuropilin is a semaphorin III receptor. Cell. 1997;90:753–762. - PubMed
-
- Chen H, Chédotal A, He Z, Goodman CS, Tessier-Lavigne M. Neuropilin-2, a novel member of the neuropilin family, is a high affinity receptor for the semaphorins Sema E and Sema IV but not Sema III. Neuron. 1997;19:547–559. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
